全局 API
应用实例 API
调用 createApp 返回一个应用实例,该实例提供了一个应用上下文, 应用实例挂载的整个组件树共享相同的上下文
createApp()
创建一个应用实例
- 参数
- {Object} rootComponent 根组件选项
- {Object} rootProps 传递给根组件的 props
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp(
{
},
{
}
);
|
createSSRApp()
以 SSR 模式创建一个应用实例, 用法和 createApp() 相同
app.mount()
将应用实例挂载到一个容器元素中
- 参数可以是一个实际的 DOM 元素或一个 CSS 选择器, 返回根组件实例
- 如果该组件有
template 模板或定义了 render 函数, 则替换容器内所有现存的 DOM 节点, 否则使用容器元素的 innerHTML 作为模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
import App from './App.vue';
const app = createApp({
});
app.mount(App);
|
app.unmount()
卸载一个已挂载的应用实例, 同时触发该应用组件树内所有组件的卸载生命周期钩子
app.onUnmount()
Vue 3.5 支持
注册一个回调函数, 在应用卸载时调用
1
2
3
| app.onUnmount(() => {
})
|
app.component()
注册或查找全局组件, 根据参数个数区分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp();
app.component('my-component', {
});
app.component('my-component');
|
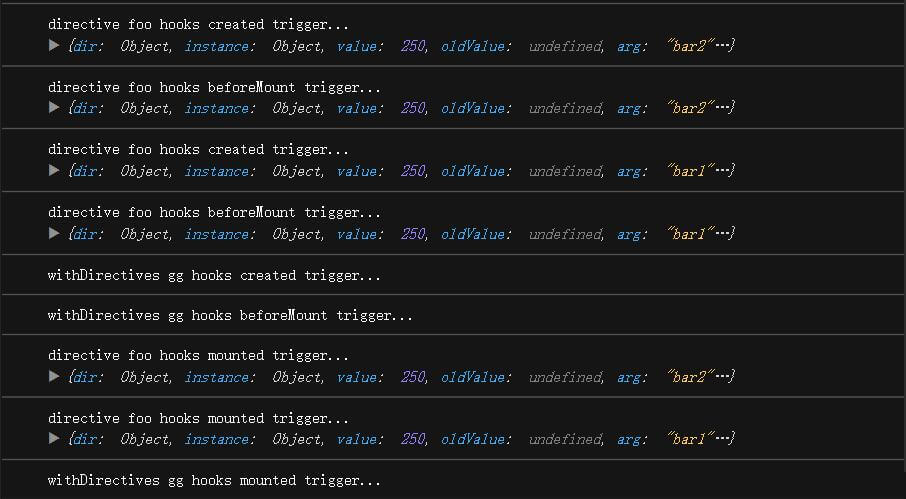
app.directive()
注册或查找全局指令, 根据参数个数区分
自定义指令主要是为了重用涉及普通元素的底层 DOM 访问的逻辑
只有当所需功能只能通过直接的 DOM 操作来实现时, 才应该使用自定义指令
一个自定义指令由一个包含类似组件生命周期钩子的对象来定义
当在组件上使用自定义指令时, 它会始终应用于组件的根节点
如果组件存在多个根节点时, 指令将会被忽略并且抛出一个警告
钩子参数
- el 指令绑定的元素, 可用于直接操作 DOM
- binding 一个对象
- value 传递给指令的值, 例如
v-my-directive="1 + 1" 的值为 2
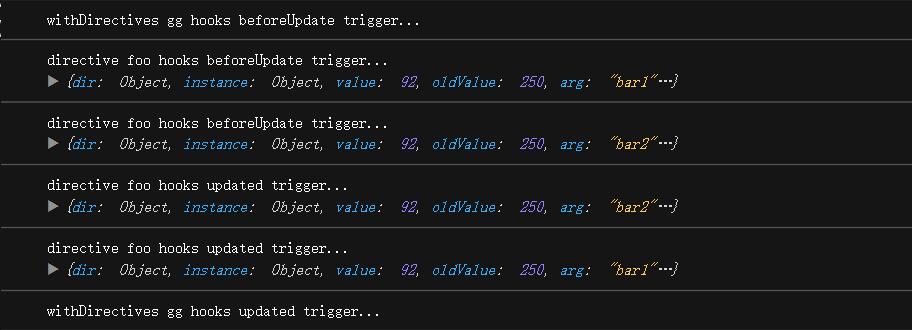
- oldValue 之前的值, 仅在
beforeUpdate 和 updated 中可用
- arg 传递给指令的参数, 例如
v-my-directive:name 的参数为 name
- modifiers 一个包含修饰符的对象, 例如
v-my-directive.foo.bar 的修饰符对象为 {foo: true, bar: true}
- instance 使用该指令的组件实例
- dir 指令的定义对象
- vnode 代表绑定元素的底层 VNode
- prevVnode 之前的渲染中代表指令所绑定元素的 VNode, 仅在
beforeUpdate 和 updated 中可用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <template>
<MyComponent v-my-directive:name.foo.bar="test" />
</template>
<script>
import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp();
app.directive('my-directive', {
});
app.directive('my-directive', (el, binding) => {
});
</script>
|
app.use()
安装一个 插件, 插件可以是一个包含 install() 方法的对象或者是一个安装函数本身
- 参数
- 第一个参数为插件本身
- 可选, 第二个参数作为插件选项将会传递给插件的
install()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp();
const myPlugins = {
install(app, options) {
},
};
app.use(myPlugins, {
name: 'hello world',
});
app.use((app, options) => {
});
|
app.mixin()
不推荐使用
应用一个全局的 mixin, 作用于应用中的每个组件实例 (不推荐使用), 在 Vue 3 中为了向后兼容
app.provide()
提供一个值, 可以在应用中的所有后代组件中注入使用
- 参数
- key, 注入的 key
- value, 注入的 key 对应的值, 返回应用实例本身
1
2
3
4
5
6
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp({
inject: ['name'],
template: '<span>{{name}}</span>',
});
app.provide('name', 'hello world');
|
app.runWithContext()
Vue 3.3 支持
使用当前应用作为注入上下文执行回调函数, 在回调同步调用期间, 即使没有当前活动的组件实例, inject() 调用也可以从当前应用提供的值中查找注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { inject } from 'vue';
app.provide('id', 1);
const injected = app.runWithContext(() => {
return inject('id');
});
console.log(injected);
|
app.version
提供当前应用所使用的 Vue 版本号, 插件中可根据此执行不同的逻辑
app.config
应用实例暴露出的一个 config 对象, 其中包含了对此应用实例的配置
app.config.errorHandler
用于为应用实例内抛出的未捕获错误指定一个全局处理函数
app.config.warnHandler
用于为 Vue 的运行时警告指定一个自定义处理函数
设置为 true 可在浏览器工具的 性能/时间线 页启用对组件初始化、编译、渲染和修改的性能表现追踪
app.config.compilerOptions
配置 运行时编译器 的选项
app.config.compilerOptions.isCustomElement 用于指定一个检查方法来识别原生自定义元素
app.config.compilerOptions.whitespace 用于调整模板中空格的处理行为 condense(default) | preserve
app.config.compilerOptions.delimiters 用于调整模板内文本插值的分隔符, 默认 [‘, ‘]
app.config.compilerOptions.comments 用于调整是否移除模板中的 HTML 注释
app.config.globalProperties
用于注册能够被应用实例内所有组件实例访问到的全局属性的对象, 对 Vue 2 中 Vue.prototype 使用方式的一种替代
app.config.optionMergeStrategies
用于定义自定义组件选项的合并策略的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import { createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp();
app.config.errorHandler = (err, instance, info){}
app.config.globalProperties.name = "hello world"
app.config.globalProperties.$xhr = () => {};
app.config.compilerOptions.isCustomElement = (tag){
return tag.startsWith('icon-');
}
|
app.config.idPrefix
Vue 3.5 支持
配置此应用中通过 useId() 生成的所有 ID 的前缀
app.config.throwUnhandledErrorInProduction
Vue 3.5 支持
强制在生产模式下抛出未处理的错误
通用
version
暴露当前所使用的 Vue 的版本号
nextTick()
Dom 更新不是同步的, Vue 会在 next tick 更新周期中缓冲所有状态的修改, 以确保进行了多次状态修改, 每个组件都只会被更新一次
等待下一次 DOM 更新刷新的工具方法, 可以在状态改变后立即使用以等待 DOM 更新完成
- 传递一个回调函数作为参数
- 或者 await 返回的 Promise
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { version, nextTick } from 'vue';
console.log(version);
async function increment() {
console.log('DOM 还未更新');
await nextTick();
console.log('DOM 已更新');
}
|
defineComponent()
创建一个合成类型的构造函数, 用于手动渲染函数、TSX 和 IDE 工具支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import { createApp, defineComponent } from 'vue';
const MyComponent = defineComponent({
data() {
return { count: 1 };
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.count++;
},
},
});
const app = createApp(MyComponent).mount('#app');
|
- Vue 3.3 支持, 备用签名, 旨在与组合式 API和渲染函数或 JSX 一起使用
- 参数为 setup 函数, 函数名称作为组件名称使用, 第二个可选参数为其它选项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import { createApp, defineComponent, ref, h } from 'vue';
const HelloWorld = defineComponent((props, ctx) => {
const count = ref(0);
return () => h('div', count.value);
}, {
props: {
foo: {
type: String,
default: 'Hello Foo',
},
visible: {
type: Boolean,
default: false,
},
},
});
const app = createApp(HelloWorld).mount('#app');
|
defineAsyncComponent()
创建一个只有在需要时才会加载的异步组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent({
loader: () => import('./Foo.vue')
loadingComponent: LoadingComponent,
errorComponent: ErrorComponent,
delay: 200,
timeout: 3000,
suspensible: false,
onError(error, retry, fail, attempts) {
if (error.message.match(/fetch/) && attempts <= 3) {
retry()
} else {
fail()
}
}
});
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import { defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
const AsyncComp = defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./components/AsyncComponent.vue');
);
app.component('async-component', AsyncComp);
import { createApp, defineAsyncComponent } from 'vue';
createApp({
components: {
AsyncComponent: defineAsyncComponent(() =>
import('./components/AsyncComponent.vue');
),
},
});
|
和 defineComponent() 接收的参数相同, 返回值是一个可以通过 customElements.define() 注册的自定义元素构造器(继承自 HTMLElement)
这些属性也可以作为第二个参数传递
- configureApp 一个函数, 可用于配置自定义元素的 Vue 应用实例. Vue 3.5 支持
- shadowRoot boolean, 默认为 true, 设置为 false 以在不带 shadow root 的情况下渲染自定义元素, 自定义元素组件中的 <style> 将不再被封装隔离. Vue 3.5 支持
- nonce string, 如果提供, 将在注入到 shadow root 样式标签上设置 nonce attribute. Vue 3.5 支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import { defineCustomElement } from 'vue';
const MyVueElement = defineCustomElement({
props: {},
emits: {},
template: `...`,
styles: [`/* inlined css */`],
});
const MyNewElement = defineCustomElement(MyVueElement, {
configureApp(app){
app.name = 'MyVueElement'
},
nonce: 'noncemyvueelement'
})
customElements.define('my-new-element', MyNewElement);
|
组合式 API
组合式函数(Composables) 是一个利用 Vue 的组合式 API 来封装和复用有 状态逻辑 的函数
组合式 API 的核心思想是直接在函数作用域内定义响应式状态变量, 并将从多个函数中得到的状态组合起来处理复杂问题, 这种形式更加自由灵活和高效.
组合式 API(composition API) 是一系列 API 的集合, 能够通过函数而不是声明选项的方式书写 Vue 组件来实现更加简洁高效的逻辑复用(选项式 API 中主要的逻辑复用机制是 mixins), 涵盖以下方面的 API
setup()
对于结合单文件组件使用的组合式 API 推荐使用 <script setup> 语法
setup() 钩子是在组件中使用 组合式 API 的入口, 通常在两个情况下使用
基本使用
在创建组件实例时, 在初始 prop 解析之后立即调用 setup
在生命周期方面, 在 beforeCreate 钩子之前调用
getCurrentInstance
- 支持访问内部组件实例,用于高阶用法或库的开发
- 只能在 setup 或生命周期钩子中调用
setup() 应该同步地返回一个对象, 唯一可以使用 async setup() 的情况是该组件是 <Suspense> 组件地后裔
访问 Props
setup() 的第一个参数, 是响应式地并且会在传入新的 props 时同步更新- 不能直接对 props 进行解构操作, 会丢失响应性, 可以通过
toRefs() 和 toRef() 工具函数辅助完成
上下文
setup() 的第二个参数为一个上下文对象, 暴露了其他一些在 setup() 中可能会用到的值, 该上下文对象是非响应式的, 可以安全地解构, attrs 和 slots 都是非响应式的, 如果需要根据 attrs 或 slots 的改变执行副作用, 需要在 onBeforeUpdate 钩子中执行相关逻辑
- attrs 透传 Attributes, 等价于 $attrs, 除了组件声明的
props 和 emits 之外的其他 attribute
- 当一个组件以单个元素为根作渲染时, 透传的 attribute 会自动被添加到根元素上, 如果有多个根节点时没有自动 attribute 透传行为, 如果 $attrs 没有被显式绑定将会抛出一个运行时警告
- 深层组件继承时, 透传的 attribute 不会包含子组件上声明过的 props 或者针对 emits 声明事件的 v-on 侦听函数
- slots 插槽, 等价于 $slots
- emit 触发事件, 等价于 $emit
- expose 用于显示的限制该组件暴露出的属性, 父组件将仅能访问 expose 函数暴露出的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import { ref, createApp } from 'vue';
const app = createApp({
setup(props, { emit, expose }) {
const publicCount = ref(0);
expose({ count: publicCount });
emit('my-event', { name: 'hello world' });
return { publicCount };
},
});
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| import { createApp, defineComponent, h } from 'vue';
const HelloWorld = defineComponent((props, { slots }) => {
return () => [
h(
'p',
slots?.default?.() || 'rendered content from self by default slot...'
),
h(
'p',
slots?.header?.() || 'rendered content from self by header slot...'
),
];
}, {
});
const app = createApp({
setup(props, { slots }) {
return () =>
h(
HelloWorld,
{
'onVue:before-mount': () => {
console.log('child component hooks triggered...');
},
},
{
default: () =>
'rendered content from father component by default slot...',
header: () =>
h(
'span',
'rendered content from father component by header slot...'
),
}
);
},
});
app.component('hello-world', HelloWorld);
app.mount('#app');
|
使用 slotscope 渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| import { createApp, defineComponent, h } from 'vue';
const HelloWorld = defineComponent((props, { attrs, slots }) => {
const message = 'from hello world component';
const age = attrs.age > 0 ? attrs.age : 18;
console.log(props);
console.log(slots);
console.log(attrs);
return () => h('p', slots.default({ message: message, age: age }));
}, {
});
const app = createApp({
setup(props, ctx) {
return () =>
h(
HelloWorld,
{ name: 'from createApp', age: -1 },
(slotScope) =>
slotScope.message + ' - ' + slotScope.age + ' - others from createApp'
);
},
});
app.component('hello-world', HelloWorld);
app.mount('#app');
|
返回渲染函数将会阻止返回其他东西, 对于父组件通过模板引用组件暴露的属性使用 expose() 方法解决
- 返回一个 渲染函数, 此时在渲染函数中可以直接使用在同一作用域下声明的响应式状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import { h, ref, reactive } from 'vue';
const app = createApp({
setup(props, { expose }) {
const count = ref(0);
const object = reactive({ foo: 'bar' });
const increment = () => ++count.value;
expose({ increment });
return () => h('div', [count.value, object.foo]);
},
});
|
响应式: 核心
- 响应式状态默认是深层次的, 即对深层次的响应式状态的更改也能被检测到
- 只有代理对象是响应式的, 更改原始对象不会触发更新, 使用响应式系统时仅使用声明对象的代理版本
ref()
当在模板中使用了一个 ref, 然后改变这个 ref 的值, Vue 会自动检测到这个变化并相应地更新 DOM, 这个过程通过一个基于依赖追踪的响应式系统实现的, 当一个组件首次渲染时, Vue 会追踪在渲染过程中使用的每一个 ref, 当一个 ref 被修改时, 它会触发追踪它的组件的一次重新渲染, 在标准的 javascript 中无法检测普通变量的修改, 可以通过 getter 和 setter 方法来拦截对象属性的 get 和 set 操作.
.value 属性给予了 Vue 一个机会来检测 ref 何时被访问或修改, 在其内部, Vue 在它的 getter 中执行追踪, 在它的 setter 中执行触发, 概念上 ref 可以看作是一个这样的对象.
接受一个内部值, 返回一个响应式可更改的 ref 对象, 此对象只有一个指向其内部值的属性 .value
- 将一个对象赋值给 ref, 那么这个对象将通过
reactive() 转为具有深层次响应式的对象, 如果对象中包含了嵌套的 ref, 它们将被深层地解包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import { ref } from 'vue';
const obj = ref({
nested: { count: 0 },
arr: ['foo', 'bar'],
});
obj.value.nested.count++;
obj.value.arr.push('baz');
|
- 一个包含对象类型值的 ref 可以响应式的替换整个对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const count = ref(0);
console.log(count.value);
count.value++;
console.log(count.value);
const objRef = ref({ count: 0 });
objRef.value = { count: 1 };
|
- ref 被传递给函数或是从一般对象上被解构时, 不会丢失响应性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| const obj = {
foo: ref(0),
bar: ref(1),
};
callSomeFn(obj.foo);
const { foo, bar } = obj;
|
- 当 ref 在模板中作为顶层属性被访问时, 它们会被自动解包, 不需要使用
.value
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const obj = { foo: ref(1) };
const count = ref(0);
function increment() {
count.value++;
}
</script>
<template>
<button @click="increment">{{count}}</button>
<p>{{obj.foo.value}}</p>
</template>
|
computed()
返回一个只读的响应式 ref 对象, 该 ref 通过 .value 暴露 getter 函数的返回值
- 接受一个 getter 函数
- 接受一个带有 get 和 set 函数的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
const count = ref(1);
const plusOne = computed(() => count.value + 1);
console.log(plusOne.value);
plusOne.value++;
const count = ref(1);
const plusOne = computed({
get: () => count.value + 1,
set: (val) => {
count.value = val - 1;
},
});
plusOne.value = 1;
console.log(count.value);
|
reactive()
返回一个对象的响应式代理
- 对同一个原始对象调用
reactive() 总是返回同样的代理对象
- 对一个已存在的代理对象调用
reactive() 总是返回其本身
局限性
- 有限的值类型: 只能用于对象类型(对象、数组、Map、Set 这样的集合类型), 不能持有
string, number, boolean 这样的原始类型
- 不能替换整个对象: 因为 Vue 的响应式系统是通过属性访问进行追踪的, 因此需要始终保持对响应式对象的相同引用,
- 对解构操作不友好: 将响应式对象的属性赋值或解构至本地变量时、或是将该属性传入一个函数时将失去响应性
==建议使用 ref() 作为生命响应式状态的主要 API==
- 将一个 ref 作为响应式对象的属性被访问或修改时自动解包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| const count = ref(0);
const state = reactive({
count,
});
console.log(state.count);
console.log(state.count === count.value);
count.value++;
console.log(count.value, state.count);
state.count++;
console.log(count.value, state.count);
|
- 将一个新的 ref 赋值给一个关联了已有 ref 的属性, 那么旧的 ref 会被替换
1
2
3
| const otherCount = ref(4);
state.count = otherCount;
console.log(count.value, state.count);
|
- 只有当嵌套在一个深层响应式对象内时, 才会发生 ref 解包, 当其作为 浅层响应式对象 的属性被访问时不会被解包
- 当 ref 作为响应式数组或原生集合类型(如 Map)中的元素被访问时, 不会被解包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import { shallowReactive, reactive, ref } from 'vue';
const sr = shallowReactive({
arr: ref([1, 2, 3]),
});
console.log(sr.arr.value[0]);
const books = reactive([ref('Vue 3.0')]);
console.log(books[0].value);
const map = reactive(new Map([['count', ref(0)]]));
console.log(map.get('count').value);
|
readonly()
- 接受一个对象(响应式或普通)或一个 ref, 返回原值的只读代理
- 任何被访问的嵌套属性也是只读的, 它的 ref 解包行为与 reactive() 相同, 但解包得到的值是只读的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import { reactive, readonly, watchEffect } from 'vue';
const original = reactive({ count: 0 });
const copy = readonly(original);
watchEffect(() => {
console.log(copy.count);
});
original.count++;
copy.count++;
|
watch()
- 侦听一个或多个响应式数据源, 并在数据源变化时调用所给的回调函数, 使用方式和 this.$watch 和 watch 选项完全等效
- 默认是浅层侦听, 仅在侦听的属性被赋新值时才触发回调, 而嵌套属性的变化不会触发, 如果需要侦听嵌套属性, 使用
deep: true 选项
- 默认是懒侦听的, 仅在侦听源发生变化时才触发回调, 如果需要在创建侦听器时立即执行一遍回调, 使用
immediate: true 选项
参数
第一个参数是侦听器的源, 支持包含返回值的函数、ref、响应式对象、或者以上类型的值组成的数组
第二个参数是侦听源发生变化时调用的函数, 函数接收三个参数: 新值、旧值,及一个用于注册副作用清理的回调函数
第三个参数是一个配置项对象
- immediate 在侦听器创建时立即触发回调, 第一次调用时旧值为
undefined
- deep 如果源是对象, 强制深度遍历, 以便在深层级变更时触发回调
- flush 调整回调函数的刷新时机, 见 watchEffect()
- onTrack/onTrigger 调试侦听器的依赖, 见 watchEffect()
- once 回调函数只会执行一次, 侦听器将在回调函数首次运行后自动停止, Vue 3.4 支持
暂停/恢复侦听器, Vue 3.5 支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| import { reactive, ref, watch, onWatcherCleanup } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({ count: 0 });
watch(
() => state.count,
(newVal, oldValue) => {
},
{
deep: true,
once: true,
}
);
const count = ref(0);
watch(count, (count, prevCount) => {
});
const stop = watch([fooRef, barRef], ([foo, bar], [prevFoo, prevBar]) => {
});
stop();
watch(id, async (newValue, oldValue, onCleanup) => {
const { response, cancel } = doAsyncWork(newValue);
onCleanup(cancel);
data.value = await response;
});
const {stop, pause, resume} = watch(id, async ()=>{
const { response, cancel } = doAsyncWork(id.value);
onWatcherCleanup(cancel);
});
pause();
resume();
stop();
|
- 惰性执行副作用
- 更具体地说明应触发侦听器重新运行的状态
- 访问被侦听状态的先前值和当前值
- 侦听多个源
watchEffect()
立即执行一个函数, 同时响应式地追踪其依赖, 并在依赖更新时重新执行函数
- 第一个参数是要运行的副作用函数, 该函数接收一个函数用来注册清理回调, 清理回调会在该副作用函数下一次执行之前被调用
- 第二个参数是可选项, 用来调整副作用的刷新时机或调试副作用的依赖
- 返回值
- 一个用来停止该副作用的函数
- 暂停/恢复侦听器, Vue 3.5 支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| const count = ref(0);
const stop = watchEffect(
(onCleanup) => {
console.log(count.value);
},
{
flush: 'pre',
onTrick(e) {},
onTrigger(e) {},
}
);
count.value++;
stop();
const {stop, pause, resume} = watchEffect(() => { });
pause();
resume();
stop();
|
副作用刷新时机, 会在组件更新之前执行副作用
- 如果需要在组件更新后重新运行侦听器副作用
- flush
- pre: ‘默认值’, 指定的回调应该在渲染前被调用
- post: 将回调推迟到渲染之后调用, 注意:这也将推迟副作用的初始运行,直到组件的首次渲染完成。
- sync: ‘始终同步触发’, 低效
副作用清除 onCleanup
- 副作用即将重新执行时
- 侦听器被停止(setup 或 lifeCycle Hooks 中使用过, 则在组件卸载时)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| watchEffect(async (onCleanup) => {
const { response, cancel } = doAsyncWork(id.value);
onCleanup(cancel);
data.value = await response;
});
|
- 侦听器调试, 只能用于开发模式下
- onTrack 响应式 property 和 ref 作为依赖项被追踪时被调用
- onTrigger 依赖项变更导致副作用被触发时被调用
watchEffect() 使用 flush: ‘post’ 选项时的别名
watchEffect() 使用 flush: ‘sync’ 选项时的别名
onWatcherCleanup()
Vue 3.5 支持
注册一个清理函数, 在当前侦听器即将重新运行时执行, 只能在 watchEffect 作用函数或 watch 回调函数的同步执行期间调用(不能在异步函数中调用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import {watch, onWatcherCleanup} from 'vue';
watch(id, (newId) => {
const {response, cancel} = doAsyncWork(newId);
onWatcherCleanup(cancel)
})
|
响应式: 工具
isRef()
检查某个值是否是 ref
unref()
如果参数是 ref, 则返回 ref 指向的内部值, 否则返回参数本身. 是 isRef(val) ? val.value : val 的一个语法糖
toRef()
将值、refs 或 getters 规范化为 refs(Vue 3.3 支持)
基于响应式对象上的一个属性, 新创建一个对应的 ref, 此 ref 与其源属性保持同步, 改变源属性的值将更新 ref 的值, 反之亦然
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import { reactive, toRef } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({ foo: 1, bar: 2 });
const fooRef = toRef(state, 'foo');
fooRef.value++;
console.log(state.foo);
state.foo++;
console.log(fooRef.value);
|
toValue()
Vue 3.3 支持
将值、refs 或 getters 规范化为值, 与 unref() 类似, 不同的是此函数也会规范化 getter 函数, 如果参数是一个 getter, 它将会被调用并且返回它的返回值
1
2
3
4
| import { toValue, ref } from 'vue';
toValue(1);
toValue(ref(1));
toValue(() => 1);
|
toRefs()
方便消费组件可以在不丢失响应性的情况下对返回的对象进行分解/扩散
将一个响应式对象转换为一个普通对象, 这个普通对象的每个属性都指向源对象相应属性的 ref, 每个单独的 ref 都是使用 toRef() 创建的
- toRefs 在调用时只为源对象上的可以枚举的属性创建 ref, 如果为可能还不存在的属性创建 ref 时, 使用 toRef
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| import { reactive, toRefs } from 'vue';
const state = reactive({ foo: 1, bar: 2 });
const stateAsRefs = toRefs(state);
state.foo++;
console.log(stateAsRefs.foo.value);
stateAsRefs.foo.value++;
console.log(state.foo);
|
isProxy()
检查一个对象是否由 reactive(), readonly(), shallowReactive(), shallowReadonly() 创建的代理
isReactive()
检查一个对象是否由 reactive(), shallowReactive() 创建的代理
isReadonly()
检查对象是否是由 readonly(), shallowReadonly() 创建的只读代理, 只读对象的属性可以更改, 但不能通过传入的对象直接赋值
响应式: 进阶
shallowRef()
ref() 的浅层作用形式
- 浅层 ref 的内部值将会原样存储和暴露, 并且不会被深层递归地转为响应式
- 只有对
.value 的访问是响应式的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { shallowRef } from 'vue';
const state = shallowRef({ count: 1 });
state.value.count = 2;
state.value = { count: 2 };
|
triggerRef()
强制触发依赖一个 浅层 ref 的副作用, 通常对浅引用的内部值进行深度变更后使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import { shallowRef, watchEffect, triggerRef } from 'vue';
const shallow = shallowRef({ name: 'hello world' });
watchEffect(() => {
console.log(shallow.value.name);
});
shallow.value.name = 'hello gg';
triggerRef(shallow);
|
customRef()
它需要一个工厂函数,该函数接收 track 和 trigger 函数作为参数,并且应该返回一个带有 get 和 set 的对象
创建一个自定义的 ref, 显式声明对其依赖追踪和更新触发的控制方式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| <template> <input v-model="text" /> </template>
<script setup>
const text = useDebouncedRef('hello');
</script>
<script>
import { customRef } from 'vue';
function useDebouncedRef(value, delay = 200) {
let timeout;
return customRef((track, trigger) => {
return {
get() {
track();
return value;
},
set(newValue) {
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(() => {
value = newValue;
trigger();
}, delay);
},
};
});
}
</script>
|
shallowReactive()
reactive() 的浅层作用形式
- 没有深层级的转换, 浅层响应式对象里只有根级别的属性是响应式的
- 属性的值会被原样存储和暴露, 值为 ref 的属性不会自动解包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { shallowReactive, isReactive } from 'vue';
const state = shallowReactive({ foo: 1, nested: { bar: 2 } });
state.foo++;
isReactive(state.nested);
state.nested.bar++;
|
shallowReadonly()
readonly() 的浅层作用形式
- 没有深层级的转换, 只有根层级的属性变为了只读
- 属性的值会被原样存储和暴露, 值为 ref 的属性不会自动解包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| import { shallowReadonly, isReadonly } from 'vue';
const state = shallowReadonly({ foo: 1, nested: { bar: 2 } });
state.foo++;
isReadonly(state.nested);
state.nested.bar++;
|
toRaw()
可用于临时读取数据而无需承担代理访问/跟踪开销,也可用于写入数据而避免触发更改. 不建议保留对原始对象的持久引用
返回由 reactive(), readonly(), shallowReactive(), shallowReadonly() 创建的的代理对应的原始对象
1
2
3
| const foo = {};
const reactiveFoo = reactive(foo);
console.log(toRaw(reactiveFoo) === foo);
|
markRaw()
将一个对象标记为不可转为代理并返回该对象本身
- 有些值不应该是响应式的,例如复杂的第三方类实例或 Vue 组件对象
- 当渲染具有不可变数据源的大列表时,跳过代理转换可以提高性能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { markRaw, reactive, isReactive } from 'vue';
const foo = markRaw({});
console.log(isReactive(reactive(foo)));
const bar = reactive({ foo });
console.log(isReactive(bar.foo));
|
effectScope()
创建一个 effect 作用域, 可以捕获其中所创建的响应式副作用(计算属性和侦听器), 这样捕获到的副作用可以一起处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import { effectScope, watch, watchEffect } from 'vue';
const scope = effectScope();
scope.run(() => {
const doubled = computed(() => counter.value * 2);
watch(doubled, (newValue, oldValue) =>
console.log(doubled.value, newValue, oldValue)
);
watchEffect(() => console.log('Count: ', doubled.value));
});
scope.stop();
|
如果存在则返回当前活跃的 effect 作用域
此方法可以作为可复用的组合式函数中 onUnmounted 的替代品, 它并不与组件耦合, 因为每个 Vue 组件的 setup 函数也是在一个 effect 作用域中调用的
在当前活跃的 effect 作用域上注册一个处理回调函数, 当相关的 effect 作用域停止时会调用注册的回调函数, 这个方法可以作为可复用的组合式函数中的 onUnmounted 的替代
1
2
3
4
5
| import { onScopeDispose } from 'vue';
onScopeDispose(() => {
console.log('活跃的 effect 作用域被停止...');
});
|
生命周期钩子
所有生命周期钩子函数必须在组件的 setup() 阶段同步调用
onBeforeMount()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件 挂载之前 调用, 组件已经完成其响应式状态的设置, 但还没有创建 DOM 节点
onMounted()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件 挂载完成 之后执行
- 其所有同步子组件都已经被挂载(不包含 异步组件 或 <Suspense> 树内的组件)
- 其自身的 DOM 树已经创建完成并插入了父容器中, 仅当根容器存在于文档中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <template>
<div ref="el"></div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted } from 'vue';
const el = ref();
onMounted(() => {
console.log(el.value);
});
</script>
|
onBeforeUpdate()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件因为响应式状态变更而更新其 DOM 树之前调用
onUpdated()
父组件的更新钩子在其子组件的更新钩子之后调用, 钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件因为响应式状态变更而更新其 DOM 树之后调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <template>
<button id="count" @click="count++">{{count}}</button>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onUpdated } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0);
onUpdated(() => {
console.log(document.getElementById('count').textContent);
});
</script>
|
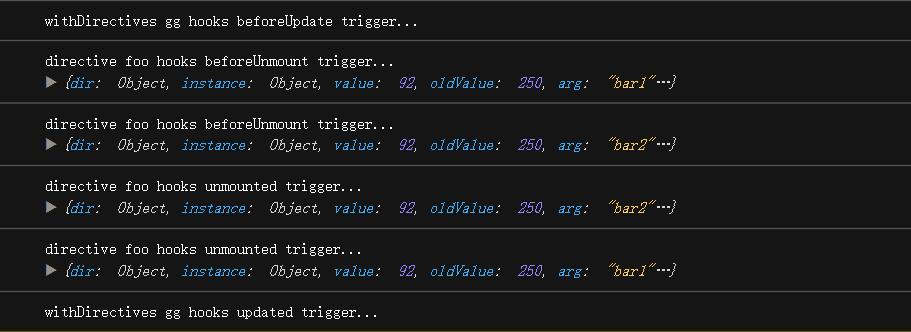
onBeforeUnmount()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件实例被 卸载之前 调用, 此时组件实例还保有全部的功能
onUnmounted()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件实例被 卸载之后 调用
- 其所有子组件都已经被卸载
- 所有相关的响应式作用(渲染作用 以及
setup() 时创建的计算属性和侦听器)都已经停止
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <script setup>
import { onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue';
let intervalId;
onMounted(() => {
intervalId = setInterval(() => {
});
});
onUnmounted(() => clearInterval(intervalId));
</script>
|
onActivated()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数, 如果组件实例是 <KeepAlive> 缓存树的一部分, 当组件被插入到 DOM 中时调用
onDeactivated()
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数, 如果组件实例是 <KeepAlive> 缓存树的一部分, 当组件从 DOM 中移除时调用
onErrorCaptured()
注册一个回调函数在捕获了后代组件传递的错误时调用
错误来源
- 组件渲染
- 事件处理器
- 生命周期钩子
setup() 函数- 侦听器
- 自定义指令钩子
- 过渡钩子
函数参数包含三个, 通过返回 false 阻止错误继续向上传递
- 错误对象
- 触发该错误的组件实例
- 说明错误来源类型的的信息字符串
错误传递规则
- 默认情况下, 所有的错误都会被发送到应用级
app.config.errorHandler(前提已经定义), 这样这些错误都能在一个统一的地方报告给分析服务
- 如果组件的继承链或组件链上存在多个
errorCaptured 钩子, 对于同一个错误, 这些钩子会被按从底到上的顺序一一调用, 这个过程称为 向上传递, 类似于原生 DOM 事件的冒泡机制
- 如果
errorCaptured 钩子本身抛出了一个错误, 那么这个错误和原来捕获到的错误都将被发送到 app.config.errorHandler
errorCaptured 钩子可以通过返回 false 来阻止错误继续向上传递
onRenderTracked()
仅在开发模式下可用, 且在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件渲染过程中追踪到响应式依赖时调用
onRenderTriggered()
仅在开发模式下可用, 且在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
注册一个回调函数在组件的响应式依赖的变更触发了组件渲染时调用
onServerPrefetch()
注册一个异步函数, 在组件实例在服务器上被渲染之前调用, 可用于执行一些仅存在于服务端的数据抓取过程
- 如果返回一个 Promise, 服务端渲染会在渲染该组件前等待该 Promise 完成
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <script setup>
import { ref, onServerPrefetch, onMounted } from 'vue';
const data = ref(null);
onServerPrefetch(async () => {
data.value = await fetchOnServer();
});
onMounted(() => {
if(!data.value) {
data.value = await fetchOnClient();
}
});
</script>
|
VNode 生命周期事件
VNode 生命周期事件前缀从 hook: 更改为 vue:, 这些事件也可用于 HTML 元素, 和在组件上的用法一样
vue: 前缀为固定格式, 生命周期事件名可以使用 kebab-case 或者 camelCase 格式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <template>
<child-component @hook:mounted="onMounted"></child-component>
<child-component @vue:mounted="onMounted"></child-component>
<child-component @vue:before-update="onBeforeUpdate"></child-component>
<child-component @vue:beforeUpdate="onBeforeUpdate"></child-component>
</template>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| import { h, createApp, defineComponent } from 'vue';
const HelloWorld = defineComponent((props, ctx) => {
return () => h('p', 'hello world component');
}, {
});
const app = createApp({
data() {
return {};
},
template: `<h1>This is template option.</h1>
<hello-world @vue:before-mount="helloWorldBeforeMount"></hello-world>`,
methods: {
helloWorldBeforeMount() {
console.log('child component hooks before-mount triggered...');
},
},
});
app.component('hello-world', HelloWorld);
app.mount('#app');
|
依赖注入
provide()
provide() 必须在组件的 setup() 阶段同步调用
允许组件向其所有后代组件注入一个依赖, 不论组件层次深度
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <script setup>
import { ref, provide } from 'vue';
provide('name', 'hello world');
provide(() => {
return { foo: 'foo' };
});
const count = ref(0);
provide('count', count);
</script>
|
inject()
inject() 必须在组件的 setup() 阶段同步调用
注入一个由祖先组件或整个应用(通过 app.provide() ) 提供的值
第一个参数为注入的 key, 通过遍历父组件链匹配 key 来确定最近的组件所提供的值, 否则将返回 undefined
第二个参数可选, 即在没有匹配到 key 时使用的默认值,
- 如果为一个工厂函数, 则用来返回某些创建复杂的值
- 如果默认值本身是一个函数, 则需要将 true 作为第三个参数传入, 表明这个函数就是默认值而不是工厂函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <script setup>
import { inject } from 'vue';
const count = inject('count');
const foo = inject('foo', 'default value');
const bar = inject('bar', () => new Map());
const fn = inject('fn', () => {}, true);
</script>
|
hasInjectionContext()
Vue 3.3 支持
如果 inject() 可以在错误的地方被调用而不触发警告, 则返回 true. 适用于希望在内部使用 inject() 而不向用户发出警告的库.
选项式 API
选项式 API 以 组件实例 的概念为中心(this), 将响应性相关的细节抽象出来, 并强制按照选项来组织代码, 从而对初学者而言更为友好
辅助
useAttrs()
用于在 SFC 中获取 setup 上下文中的 attrs 对象
useSlots()
用于在 SFC 中获取 setup 上下文中的 slots 对象
useModel()
Vue 3.4 支持
驱动 defineModel() 的底层辅助函数, 优先使用 defineModel()
useTemplateRef()
Vue 3.5 支持
返回一个浅层 ref, 其值将与模板中的具有匹配 ref 的元素或组件同步
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <template>
<input ref="input"/>
</template>
<script setup>
import {useTemplateRef, onMounted} from 'vue';
const imputRef = useTemplateRef('input');
onMounted(() => {
inputRef.value.focus();
});
</script>
|
useId()
Vue 3.5 支持
用于为无障碍属性或表单元素生成每个应用内唯一的 ID
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| <template>
<form>
<label :for="id">Name</label>
<input :id="id" type="text"/>
</form>
</template>
<script setup>
import {useId} from 'vue';
const id = useId();
</script>
|
useHost()
Vue 3.5 支持
一个组合式 API 辅助函数, 返回当前 Vue 自定义元素的宿主元素
useShadowRoot()
Vue 3.5 支持
一个组合式 API 辅助函数, 返回当前 Vue 自定义元素的 shadow root
状态选项
data
以 _ 和 $ 开头的属性不会被组件实例代理, 因为它们可能和 Vue 的内置属性, API 方法冲突
用于声明组件初始响应式状态的函数
props
用于声明组件的 props
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
props: ['name', 'age'],
props: {
name: String,
age: {
type: Number,
default: 18,
required: true,
validator: (value) => {
return value > 0;
},
},
hobbies: {
type: Array,
default: (prop) => ['reading'],
},
},
};
|
computed
用于声明在组件实例上暴露的计算属性
- 包含一个只有 getter 函数的方法, 方法名为计算属性的名称
- 包含一个具有 get 和 set 函数的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| export default {
data() {
return { age: 18 };
},
computed: {
name() {
return 'hello world';
},
agePlus: {
get() {
return this.age;
},
set(val) {
this.age = this.age + val;
},
},
},
};
|
methods
在声明方法时避免使用箭头函数, 因为它们不能通过 this 访问组件实例
用于声明要混入到组件实例中的方法
用于声明在数据更改时调用的侦听回调
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
| export default {
data() {
return { age: 18 };
},
watch: {
age(val, oldVal) {
console.log(val, oldVal);
},
b: 'otherMethod',
c: {
handler(val, oldVal) {},
deep: true,
flush: 'post',
onTrack(e) {},
},
'c.d': function (val, oldVal) {},
e: {
handler(val, oldVal) {},
immediate: true,
},
f: [
'handler',
function handle2(val, oldVal) {
console.log('handle2 triggered');
},
{
handler: function handle3(val, oldVal) {
console.log('handle3 triggered');
},
},
],
},
};
|
emits
用于声明由组件触发的自定义事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
emits: ['check'],
emits: {
click: null,
submit: (payload) => {
if (payload.email && payload.password) {
return true;
} else {
console.warn(`Invalid submit event payload!`);
return false;
}
},
},
mounted() {
this.$emit('check');
},
};
|
expose
保持私有的内部状态或方法, 以避免紧耦合
用于声明当组件实例被父组件通过模板引用访问时暴露的公共属性, 当使用 expose 时, 只有显式列出的属性将在组件实例上暴露
1
2
3
4
5
6
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
expose: ['publicProp', 'publicMethod'],
};
|
渲染选项
template
通过 template 选项提供的模板将会在运行时即时编译
用于声明组件的字符串模板
- 如果字符串以
# 开头, 它将被用作 querySelector 的选择器, 并使用所选中元素的 innerHTML 作为模板字符串
- 如果存在
render 选项, 则 template 选项将被忽略
- 如果应用的根组件不含任何
template 或 render 选项, Vue 将尝试使用所挂载元素的 innerHTML 来作为模板
render
render 具有比 template 更高的优先级
用于编程式地创建组件虚拟 DOM 树的函数
compilerOptions
用于配置组件模板的运行时编译选项, 支持与应用级 app.config.compilerOptions 相同的选项, 并针对当前组件有更高的优先级
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import { h } from 'vue';
export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
template: '#tpl',
render() {
return h('div', {}, [h('p', 'This is tag p'), h('p', this.name)]);
},
compilerOptions: {
delimiters: ['{{', '}}'],
comments: true,
isCustomElement(tag) {
return tag.startsWith('icon-');
},
},
};
|
生命周期选项
组合式 API 中的 setup() 钩子函数会在所有 选项式 API 钩子之前调用
beforeCreate
在组件实例初始化完成之后立即调用
created
在组件实例处理完所有与状态相关的选项后调用, 此时挂载阶段还未开始, $el 属性仍不可用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件被 挂载之前 调用, 组件已经完成了其响应式状态的设置, 但还没有创建 DOM 节点, 将首次执行 DOM 渲染过程
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件被 挂载之后 调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件因为响应式状态变更而更新其 DOM 树之前调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件因为响应式状态变更而更新其 DOM 树之后调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件实例被 卸载之前 调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在组件实例被 卸载之后 调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
如果组件实例是 <KeepAlive> 缓存树的一部分, 当组件被插入到 DOM 中时调用
钩子函数在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
如果组件实例是 <KeepAlive> 缓存树的一部分, 当组件从 DOM 中移除时调用
在捕获了后代组件传递的错误时调用
仅在开发模式下可用, 且在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在一个响应式依赖被组件的渲染作用追踪后调用
仅在开发模式下可用, 且在服务器端渲染期间不会被调用
在一个响应式依赖被组件触发了重新渲染之后调用
在组件实例在服务器上被渲染之前要完成的异步函数
组合选项
用于提供可以被后代组件注入的值
用于声明要通过从上层提供方匹配并注入当前组件的属性
- 一个字符串数组
- 一个对象
- 匹配可注入的 key(String 或者 Symbol)
- 一个对象
- from 属性表示匹配可用的注入的来源
- default 属性用作候补值, 和 props 的默认值类似
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
inject: ['foo'],
inject: {
foo: { default: 'foo' },
},
inject: {
foo: {
from: 'bar',
default: 'foo',
},
},
inject: {
foo: {
from: 'bar',
default: () => [1, 2, 3],
},
},
};
|
mixins
Mixin 钩子的调用顺序与提供它们的选项顺序相同, 且会在组件自身的钩子前调用
一个包含组件选项对象的数组, 这些选项都将被混入到当前组件的实例中(不推荐使用)
extends
extends 和 mixin 实现上几乎相同, 但是表达的目标不同, mixins 选项基本用于组合功能, extends 一般更关注继承关系, 为选项式 API设计的
要继承的 基类 组件, 同 mixins 一样, 所有选项都将使用相关的策略进行合并, 不会处理 setup() 钩子的合并
其他杂项
name
使用 name 选项可以覆盖推导出的名称, 或是在没有推导出名字是显式提供一个
用于显式声明组件展示时的名称
- 在组件自己的模板中递归引用自己时
- 在 Vue 开发者工具中的组件树显示时
- 在组件抛出的警告追踪栈信息中显示时
场景 1
使用单文件组件时, 组件会根据其文件名推导出其名称, 例如 MyComponent.vue 的文件会推导出显式名称为 MyComponent
场景 2
当使用 app.component 注册全局组件时, 这个全局 ID 会自动设置为其名称
inheritAttrs
默认情况下, 父组件传递的没有被子组件解析为 props 的 attributes 绑定会被透传
用于控制是否启用默认的组件 attribute 透传行为, 默认为 true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
<script>
export default {
inheritAttrs: false,
};
</script>
<script setup>
const msg = 'hello world';
const props = defineProps(['name', 'age']);
const emit = defineEmits(['input']);
defineExpose({ msg });
defineOptions({ name: 'Comp-A', inheritAttrs: false });
</script>
|
components
用于注册对当前组件实例可用的组件的配置对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import { h } from 'vue';
export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
components: {
Foo,
'my-component': {
setup() {
return () => h('h1', 'Register local components...');
},
},
},
};
|
用于注册对当前组件实例可用的指令的配置对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
directives: {
focus: {
},
},
};
|
组件实例
除了 $data 下的嵌套属性外, 其它的属性都是只读的
$data
从 data 选项函数返回的对象, 会被组件赋为响应式, 组件实例将会代理其数据对象的属性访问
表示组件当前已解析的 props 对象
$el
该组件实例管理的 DOM 根节点, $el 直到组件 挂载完成 之前都是 undefined
$options
已解析的用于实例化当前组件的组件选项
- 全局 mixin
- 组件
extends 的基组件
- 组件级 mixin
$parent
当前组件可能存在的父组件实例, 如果当前组件是顶层组件, 则为 null
$root
当前组件树的根组件实例, 如果当前组件实例没有父组件, 则为本身
表示父组件传入 插槽 的对象
$refs
包含 DOM 元素和组件实例的对象, 通过 模板引用 注册
$attrs
包含了组件所有透传 attributes 的对象
用于命令式地创建侦听器的 API
$emit()
在当前组件触发一个自定义事件, 任何额外的参数都将传递给事件监听器的回调函数
$forceUpdate()
强制当前组件重新渲染, 仅仅影响实例本身和插入插槽内容的子组件
和全局的 nextTick 的区别是传递给 this.$nextTick() 的回调函数会带上绑定当前组件实例上下文的 this
绑定在实例上的 nextTick() 函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| export default {
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
updated() {
this.$nextTick(() => {
console.log(this.name);
});
},
};
|
内置内容
内置指令
v-text
更新元素的文本内容
v-html
更新元素的 innerHTML
v-show
基于表达式值的真假来改变元素的可见性, 通过设置内联样式的 display CSS 属性来工作
v-if
基于表达式值的真假来条件性地渲染元素或者模板片段, 同时使用 v-if 和 v-for 时, 前者的优先级更高
v-else
表示 v-if 或 v-if / v-else-if 链式调用的块
v-for
基于原始数据多次渲染元素或模板块
v-on
和原生 DOM 事件不一样, 组件触发的事件没有冒泡机制, 只能监听直接子组件触发的事件, 平级组件或嵌套组件间通信, 应使用一个外部事件总线或全局状态管理方案
给元素绑定事件监听器, 缩写 @, 事件名称可以使用 camelCase 或 kebab-case 形式会被自动格式转换
1
2
3
4
5
| <button @click="$emit('increaseBy', 1)"></button>
<template>
<MyComponent @increase-by="(n) => count += n" />
</template>
|
内联事件处理器
事件被触发时执行的内联 javascript 语句(与 onClick 类似)
方法事件处理器
一个指向组件上定义的方法的属性名或是路径
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
<button @click="greet">Greet</button>
|
事件修饰符
- .stop 调用
event.stopPropagation()
- .prevent 调用
event.preventDefault()
- .capture 在捕获模式添加事件监听器
- .self 只有事件从元素本身发出才触发处理函数
- .{keyAlias} 只有在某些按键下触发处理函数
- .once 最多触发一次处理函数
- .passive 通过
{passive: true} 附加一个 DOM 事件
按键修饰符
- .enter
- .tab
- .delete 捕获 delete 和 backspace 两个按键
- .esc
- .space
- .up
- .down
- .left 只在鼠标左键事件触发处理函数
- .right 只在鼠标右键事件触发处理函数
- .middle 只在鼠标中键事件触发处理函数
系统按键修饰符
- .ctrl
- .alt
- .shift
- .meta
- .exact 允许控制触发一个事件所需的确定组合的系统按键修饰符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
<button @click.ctrl="onClick">click</button>
<button @click.ctrl.exact="onClick">click</button>
<button @click.exact="onClick">click</button>
|
v-bind
v-bind 的绑定顺序会影响渲染结果
动态的绑定一个或多个 attribute, 也可以是组件的 prop, 缩写 : 或 .(当使用 .prop 修饰符)
绑定修饰符
- .camel 将
kebab-case 命名的属性转变为 camelCase 命名
- .prop 强制绑定为 DOM property, 3.2 支持
- .attr 强制绑定为 DOM attribute, 3.2 支持
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <svg :view-box.camel="viewBox"></svg>
<div :someProperty.prop="someObject"></div>
<div .someProperty="someObject"></div>
|
同名缩写
Vue 3.4 支持
v-model
在表单输入元素或组件上创建双向绑定
- <input>
- <select>
- <textarea>
- components
修饰符
- .lazy 监听 change 事件而不是 input 事件
- .number 将输入的合法字符换转为数字
- .trim 移除输入内容两端空格
版本迭代
v-bind 的 .sync 修饰符和组件的 model 选项被移除, 使用 v-model 和参数代替
同一组件上可以使用多个 v-model 进行双向绑定
可自定义 v-model 修饰符
自定义组件时 v-model 的 prop 和 event 默认名称已更改
- prop:
value -> modelValue
- event:
input -> update:modelValue
migration
- 所有子组件
.sync 修饰符的部分替换为 v-model
- 未带参数的
v-model, 修改子组件的 prop -> modelValue, event -> update:modelValue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| <template>
<my-component :title.sync="pageTitle" />
<my-component :title="pageTitle" @update:title="pageTile = $event" />
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({ title: String });
const emit = defineEmits(['update:title']);
const changePageTitle = function (title) {
emit('update:title', title);
};
</script>
<template>
<ChildComponent v-model="pageTitle" />
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({ modelValue: String });
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
const changePageTitle = function (title) {
emit('update:modelValue', title);
};
</script>
|
Vue 2.0
v-model 只能使用 value 作为 prop, 并监听子组件抛出的 input 事件, 如果使用其他 prop, 必须使用 v-bind.sync 同步
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <template>
<my-component :value="pageTitle" @input="pageTitle = $event" />
<my-component v-model="pageTitle" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['value'],
created() {
this.$emit('input', 'hello value');
},
};
</script>
|
Vue 2.2
- 增加组件选项
model, 允许自定义 v-model 的 prop 和 event, 只能在组件上使用一个 model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <template>
<my-component :value="pageTitle" @change="pageTitle = $event" />
<my-component v-model="pageTitle" />
</template>
<script>
export default {
model: {
prop: 'title',
event: 'change',
},
props: {
value: String,
title: {
type: String,
default: 'Default title',
},
},
};
</script>
|
Vue 2.3
1
2
3
4
5
| <template>
<my-component :title="pageTitle" @update:title="pageTitle = $event" />
<my-component :title.sync="pageTitle" />
</template>
|
Vue 3.x
v-model 默认传递 modelValue prop, 并接收子组件抛出的 update:modelValue 事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| <template>
<my-component
:modelValue="pageTitle"
@update:modelValue="pageTitle = $event"
/>
<my-component v-model="pageTitle" />
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps(['modelValue']);
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
emit('update:modelValue', 'hello modelValue');
</script>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <template>
<my-component
:title="pageTitle"
@update:title="pageTitle = $event"
:content="pageContent"
@update:content="pageContent = $event"
/>
<my-component v-model:title="pageTitle" v-model:content="pageContent" />
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({ title: String, content: String });
const emit = defineEmits(['update:title', 'update:content']);
emit('update:title', 'hello title');
emit('update:content', 'hello content');
</script>
|
处理 v-model 修饰符
- 不带参数: 生成的 prop 名称为
modelModifiers 的对象, 包含传入的修饰符
- 带参数: 生成的 prop 名称为
arg + 'Modifiers'
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
| import { createApp, ref, h, defineComponent } from 'vue';
const WithoutArgs = defineComponent((props, { emit }) => {
console.log(props);
const emitValue = function (e) {
let value = e.target.value;
if (props.modelModifiers.capitalize) {
value = value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.slice(1);
}
emit('update:modelValue', value);
};
return () =>
h('p', [
'without args ',
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'write something...',
value: props.modelValue,
onInput: emitValue,
}),
]);
}, {
props: ['modelValue', 'modelModifiers'],
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
});
const WithArgs = defineComponent((props, { emit }) => {
console.log(props);
const emitValue = function (e) {
let value = e.target.value;
if (props.descriptionModifiers.uppercase) {
value = value.toUpperCase();
}
emit('update:description', value);
};
return () =>
h('p', [
'with args ',
h('input', {
type: 'text',
placeholder: 'write something...',
value: props.description,
onInput: emitValue,
}),
]);
}, {
props: ['description', 'descriptionModifiers'],
emits: ['update:description'],
});
const app = createApp({
setup(props, ctx) {
const v1 = ref('hello without args');
const v2 = ref('hello with args');
return () => [
h(WithoutArgs, {
modelValue: v1.value,
modelModifiers: { capitalize: true },
'onUpdate:modelValue': (value) => (v1.value = value),
}),
h(WithArgs, {
description: v2.value,
descriptionModifiers: { uppercase: true },
'onUpdate:description': (value) => (v2.value = value),
}),
];
},
});
app.mount('#app');
|
v-slot
如果混用了 具名插槽 和 默认插槽, 则需要为 默认插槽 使用显式的 <template> 标签, 直接为组件添加 v-slot 指令将导致编译错误
用于声明具名插槽或是期望接收 props 的作用域插槽, 缩写 #
限制使用
能够合法在函数参数位置使用的 js 表达式, 支持解构语法. 绑定的值是可选的(只有在给作用域插槽传递 props 才需要)
- <template>
- components(用于带有 prop 的单个默认插槽)
具名插槽
组件中包含多个插槽出口, <slot> 内置元素的特殊属性 name 用来给每个插槽分配唯一的 ID 以确定每一处要渲染的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
<div class="container">
<header>
<slot name="header"></slot>
</header>
<main>
<slot></slot>
</main>
<footer>
<slot name="footer"></slot>
</footer>
</div>
<BaseComponent>
<template #header>
</template>
<p>This is the first tag p</p>
<p>This is the second tag p</p>
<template #footer>
</template>
</BaseComponent>
|
动态插槽
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
<base-layout>
<template v-slot:[dynamicSlotName]></template>
<template #[dynamicSlotName]></template>
</base-layout>
|
作用域插槽
- 默认插槽接收 props, 通过子组件标签上的
v-slot 指令接收一个插槽 props 对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <slot text="hello text" message="hello message"></slot>
<MyComponent v-slot="slotScope">
{{slotScope.text}} - {{slotScope.message}}
</MyComponent>
|
- 具名插槽 props 可以作为
v-slot 指令的值被访问到 v-slot:name="slotScope"
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<MyComponent>
<template #header="headerScope"> {{ headerScope }} </template>
<template #default="{ message }">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
</template>
<template #footer>
<p>Here's some contact info</p>
</template>
</MyComponent>
|
v-pre
跳过该元素及其所有子元素的编译
v-once
仅渲染元素和组件一次, 并跳过之后的更新
v-memo
Vue 3.2 支持
缓存一个模板的子树, 根据传入的依赖值数组的比较结果控制子树的更新
- 如果依赖值为空数组, 功能等同于
v-once
- 结合
v-for 使用, 必须确保和 v-for 用在同一个元素上, 否则无效
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<div v-memo="[valueA, valueB]"></div>
<div v-for="item in list" :key="item.id" v-memo="[item.id === selected]">
<p>ID: {{ item.id }} - selected: {{ item.id === selected }}</p>
<p>more child nodes</p>
</div>
|
v-cloak
该指令只在没有构建步骤的环境下需要使用
用于隐藏尚未完成编译的 DOM 模板
内置组件
内置组件无需注册便可以直接在模板中使用,同时也支持 tree-shake; 仅在使用时才会包含在构建中
在 渲染函数 中使用内置组件时, 需要显式引入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import { h, KeepAlive, Transition } from 'vue';
export default {
setup(props, ctx) {
return () => h(Transition, { mode: 'out-in' } );
},
};
|
<Transition>
为单个元素或组件提供动画过渡效果
<Transition> props
- name
- css
- type
- duration
- mode
- appear
- enterFromClass
- enterActiveClass
- enterToClass
- appearFromClass
- appearActiveClass
- appearToClass
- leaveFromClass
- leaveActiveClass
- leaveToClass
<Transition> 事件
- @before-enter
- @before-leave
- @enter
- @leave
- @appear
- @after-enter
- @after-leave
- @after-appear
- @enter-cancelled
- @leave-cancelled(v-show only)
- @appear-cancelled
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<Transition>
<div v-if="ok">toggled content</div>
</Transition>
<Transition name="fade" mode="out-in" appear>
<component :is="view"></component>
</Transition>
<div id="transition-demo">
<Transition @after-enter="transitionComplete">
<div v-show="ok">toggled content</div>
</Transition>
</div>
|
<TransitionGroup>
为列表中的多个元素或组件提供过渡效果
<TransitionGroup> props
- tag 如果未定义, 则渲染为片段(fragment)
- moveClass 用于自定义过渡期间被应用的 CSS class, 使用
kebab-case 格式
<TransitionGroup> 事件
<TransitionGroup> 抛出与 <Transition> 相同的事件
<KeepAlive>
缓存包裹在其中的动态切换组件
<KeepAlive> props
- include 哪些组件实例可以被缓存
- exclude 哪些组件实例不被缓存
- max 最多可以缓存多少组件实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
<KeepAlive include="a,b">
<component :is="view"></component>
</KeepAlive>
<KeepAlive :include="/a|b/">
<component :is="view"></component>
</KeepAlive>
<KeepAlive :include="['a', 'b']">
<component :is="view"></component>
</KeepAlive>
|
<Teleport>
移动实际 DOM 节点(非销毁重建),并保持任何组件实例的活动状态
<Teleport> props
- to 必填项, 指定目标容器, 可以是选择器或实际元素
- disabled 值为 true 时, 内容将保留在其原始位置不做移动, 值可动态修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<Teleport to="#some-id" />
<Teleport to=".some-class" />
<Teleport to="[data-teleport]" />
<Teleport to="h1" />
<Teleport to="some-string" />
<button @click="open = true">Open Modal</button>
<Teleport to="body">
<div v-if="open" class="modal">
<p>Hello from the modal!</p>
<button @click="open = false">Close</button>
</div>
</Teleport>
|
<Suspense>
用于协调对组件树中嵌套的异步依赖的处理
<Suspense> props
<Suspense> 事件
- @pending 在 suspense 进入挂起状态时触发
- @resolve 在 default 插槽完成获取新内容时触发
- @fallback 在 fallback 插槽的内容显示时触发
<Suspense> 插槽
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <Suspense>
<Dashboard />
<template #fallback> Loading... </template>
</Suspense>
|
内置特殊元素
<component>, <slot>, <template> 具有类似组件的特性, 也是模板语法的一部分. 但它们并非真正的组件
同时在模板编译期间会被编译掉. 因此, 它们通常在模板中使用小写字母
<component>
用于渲染动态组件或元素的 元组件
<component> props
- is 要渲染的实际组件由
is prop 决定
- 如果是字符串时, 可以是 HTML 标签名或者组件的注册名
- 或者是直接绑定到组件的定义
<slot>
表示模板中的插槽内容出口
<slot> props
<template>
当使用内置指令而不在 DOM 中渲染元素时, <template> 标签可以作为占位符使用
内置特殊 Attributes
key
主要作为 Vue 的虚拟 DOM 算法提示, 在比较新旧节点列表时用于识别 vnode
ref
ref 数组并不保证与源数组相同的顺序
用于注册元素或子组件的 模板引用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <template>
<div ref="root">This is a root element</div>
<div v-for="item in list" ref="itemRefs">{{ item }}</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onBeforeUpdate, onUpdated, onMounted } from 'vue';
const root = ref(null);
const itemRefs = ref([]);
onBeforeUpdate(() => {
itemRefs.value = [];
});
onUpdated(() => {
console.log(itemRefs.value);
});
onMounted(() => {
console.log(root.value);
});
</script>
|
is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <template>
<component :is="Foo" />
<component :is="someCondition ? Foo : Bar" />
</template>
<script setup>
import Foo from './Foo.vue';
import Bar from './Bar.vue';
</script>
|
元素位置限制
由于 HTML 元素对于放在其中的元素类型的限制, 例如 ul, ol, table, select 等元素仅放置 li, tr, option 时才会显示, 将导致在使用带有此类限制元素的组件时出现问题.
- 用于原生元素时, 将被作为
Customized built-in element, 如果需要用 Vue 组件替换原生元素, 需要加上 vue: 前缀.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<template>
<table>
<my-row-component></my-row-component>
</table>
</template>
<template>
<table>
<tr is="vue:my-row-component"></tr>
</table>
</template>
|
单文件组件
SFC 语法定义
<template> 每个 *.vue 文件最多可以包含一个顶层 <template> 块, 包含的内容将被提取传递给 @vue/compiler-dom 编译生成为 渲染函数<script> 每个 *.vue 文件最多可以包含一个 <script> 块(使用 <script setup> 除外), 默认导出是 Vue 的组件选项对象<script setup> 每个 *.vue 文件最多可以包含一个 <script setup> 块, 此脚本块将被预处理为组件的 setup() 函数<style> 每个 *.vue 文件可以包含多个 <style> 块
src 导入
可以将单文件组件拆分成多个文件中, 使用 src 导入外部文件
1
2
3
| <template src="./template.html"></template>
<script src="./script.js"></script>
<style src="./style.css"></style>
|
<script setup>
<script setup> 是在单文件组件(SFC) 中使用 组合式 API 的编译时语法糖
<script setup> 中的代码会在每次组件实例被创建的时候执行
- 更少的样板内容, 更简洁的代码
- 能够使用纯 TypeScript 声明 props 和 自定义事件
- 更好的运行时性能(其模板会被编译成同一作用域内的渲染函数, 避免了渲染上下文代理对象)
- 更好的 IDE 类型推导性能(减少了语言服务器从代码中抽取类型的工作)
顶层绑定
任何在 <script setup> 声明的 顶层的绑定(包括变量, 函数声明, 以及 import 导入的内容)都能在模板中直接使用
响应式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue';
const count = ref(0);
const user = reactive({ name: 'hello world', age: 18 });
</script>
<template>
<button @click="count++">{{ count }}</button>
</template>
|
使用组件
单文件组件模板中使用组件可以使用 kebab-case 或者 PascalCase 两种格式, 推荐使用后者
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <script setup>
import { MyComponent } from './MyComponent.vue';
</script>
<template>
<MyComponent />
</template>
|
动态组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <script setup>
import Foo from './Foo.vue';
import Bar from './Bar.vue';
</script>
<template>
<component :is="Foo" />
<component :is="someCondition ? Foo : Bar" />
</template>
|
递归组件
一个单文件组件可以通过它的文件名被其自己所引用, 为防止具名的导入和组件自身推导的名字冲突可以使用别名的方式
1
| import { FooBar as FooBarChild } from './components';
|
命名空间组件
可以使用带 . 的组件标签来引用嵌套在对象属性中的组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <script setup>
import * as Form from './form-components';
</script>
<template>
<Form.Input>
<Form.Label>label</Form.Label>
</Form.Input>
</template>
|
本地声明自定义指令在 <script setup> 中不需要显式注册, 但必须遵循 vNameOfDirective 的命名规范
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <script setup>
const vMyDirective = {
mounted(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode){},
updated(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode){},
unmounted(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode){}
}
</script>
<template>
<h1 v-my-directive>This is a heading.</h1>
</template>
|
defineProps|defineEmits
defineProps 和 defineEmits 都是只能在 <script setup> 中使用的 编译器宏, 不需要导入直接使用, 且会随着 <script setup> 的处理过程一同被编译掉defineProps 接收和 props 选项相同的值, defineEmits 接收和 emits 选项相同的值defineProps 和 defineEmits 在选项传入后会提供恰当的类型推导- 传入
defineProps 和 defineEmits 的选项会从 setup 中提升到模块的作用域, 因此, 传入的选项不能引用在 setup 作用域中声明的局部变量
使用类型声明时的默认 props 值
defineProps 不能给使用类型声明的 props 提供默认值, 使用 withDefaults 编译器宏 解决
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import { withDefaults } from 'vue';
export interface Props {
msg?: string
labels?: string[]
}
const props = withDefaults(defineProps<Props>(), {
msg: 'hello withDefaults',
labels: () => ['one', 'two']
});
|
props|emit 类型声明
props 和 emits 都可以通过给 defineProps 和 defineEmits 传递纯类型参数的方式声明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <script setup>
const props = defineProps({ title: string, age: number });
const emit = defineEmits({
click: null,
submit: (payload) => {
if (payload.email && payload.password) {
return true;
} else {
console.warn(`Invalid submit event payload!`);
return false;
}
},
});
</script>
|
defineExpose()
使用 <script setup> 的组件是 默认关闭 的, 不会暴露任何在 <script setup> 中声明的绑定. 使用 defineExpose 显式指定组件中要暴露出去的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue';
const a = 1;
const b = ref(0);
defineExpose({ a, b });
</script>
|
defineOptions()
Vue 3.3 支持
在 <script setup> 中使用 选项式 API 的宏, 无法访问 <script setup> 中不是字面常数的局部变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| <script setup>
import { useSlots } from 'vue';
defineOptions({
name: 'Foo',
inheritAttrs: false,
});
const slots = useSlots();
</script>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Foo',
inheritAttrs: false,
};
</script>
<script setup>
import { useSlots } from 'vue';
const slots = useSlots();
</script>
|
defineSlots()
Vue 3.3 支持
只接受类型参数, 没有运行时参数. 用于为 IDE 提供插槽名称 和 props 类型检查的类型提示
1
2
3
4
5
| <script setup lang="ts">
const slots = defineSlots<{
default(props: { msg: string }): any;
}>();
</script>
|
definePropsRefs()
Vue 3.3 支持
在 <script setup> 中定义一个不会丢失响应性的解构 props 的响应式对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <script setup>
const {foo, bar} = definePropsRefs<{
foo: string,
bar: number
}>();
console.log(foo.value, bar.value);
</script>
|
defineRender()
Vue 3.3 支持
在 <script setup> 中定义一个渲染函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| <script setup>
defineRender(
<div>
<span>hello world</span>
</div>
);
defineRender(() => {
return (
<div>
<span>hello world</span>
</div>
);
});
</script>
|
defineModel()
Vue 3.4 支持
如果第一个参数为字符串字面量, 则被用作 prop 名称, 否则 prop 名称默认为 modelValue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <script setup>
const model = defineModel();
const model = defineModal({ type: String });
model.value = 'hello world';
const count = defineModel('count');
const count = defineModel('count', { type: Number, default: 0 });
count.value++;
</script>
|
底层编译器将其展开为以下内容
- 一个名为
modelValue 的 prop, 本地的 ref 的值与其同步
- 一个名为
update:modelValue 的事件, 当本地 ref 的值发生变更时触发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| <script setup>
const props = defineProps(['modelValue']);
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue']);
</script>
<template>
<input
:value="props.modelValue"
@input="emit('update:modelValue', $event.target.value)"
/>
</template>
|
修饰符和转换器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| <script setup>
const [modelValue, modelModifiers] = defineModel();
if (modelModifiers.trim) {
}
const [modelValue, modelModifiers] = defineModel({
set(value) {
if (modelModifiers.trim) {
return value.trim();
}
return value;
},
});
const [firstName, firstNameModifiers] = defineModel('firstName');
console.log(firstNameModifiers.uppercase);
const props = defineProps({
firstName: String,
firstNameModifiers: { default: () => ({}) },
});
const emit = defineEmits(['update:firstName']);
console.log(props.firstNameModifiers.uppercase);
</script>
<template>
<MyComponent v-model:first-name.uppercase="firstName" />
</template>
|
useSlots()|useAttrs()
- 在 SFC 中使用的辅助函数获取 slots 和 attrs
- 需要手动从 vue 中导入
- 返回的值和
setupContext.slots 和 setupContext.attrs 是等价的
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <script setup>
import { useSlots, useAttrs } from 'vue';
const slots = useSlots();
const attrs = useAttrs();
</script>
|
与普通 script 一起用
- 声明无法在
<script setup> 中声明的选项, 例如 inheritAttrs 或插件的自定义选项(Vue 3.3 使用 defineOptions 替代)
- 声明模块的具名导出(named exports)
- 运行只需要在模块作用域执行一次的副作用, 或是创建单例对象
顶层 await
<script setup> 中可以使用顶层 await, 结果代码会被编译成 async setup() > async setup() 必须与 <Suspense> 内置组件组合使用
1
2
3
| <script setup>
const post = await fetch('/api/post/1').then(res => res.json())
</script>
|
限制
由于模块执行语义的差异, <script setup> 中的代码依赖单文件组件的上下文, 当将其移动到外部的 .js 或 .ts 文件中时, 对于开发者和工具来说都会感到混乱. 因此, <script setup> 不能和 src 属性一起使用
CSS 功能
组件作用域
使用 scoped 后, 父组件的样式不会透传到子组件中,不过, 子组件的 根节点 会同时被父组件的作用域样式和子组件的作用域样式影响, 这样设计是为了让父组件可以从布局的角度出发, 调整其子组件根元素的样式
深度选择器
1
2
3
4
5
| <style scoped>
.a :deep(.b) {
}
</style>
|
插槽选择器
默认情况下, 作用域样式不会影响到 <slot /> 渲染出来的内容, 使用 :slotted 伪类以明确地将插槽内容作为选择器的目标
1
2
3
4
5
| <style scoped>
:slotted(div) {
color: red;
}
</style>
|
全局选择器
1
2
3
4
5
| <style scoped>
:global(.red) {
color: red;
}
</style>
|
css Modules
一个 <style module> 标签会被编译成 CSS Modules 并且将生成的 CSS class 作为 $style 对象暴露给组件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <template>
<p :class="$style.red">This is should be red.</p>
</template>
<style module>
.red {
color: red;
}
</style>
|
自定义注入名称
module 属性可以接受一个值作为自定义注入名称代替 $style
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <template>
<p :class="classes.red">This is should be red.</p>
</template>
<style module="classes">
.red {
color: red;
}
</style>
|
- 使用
useCssModule API 在 setup() 和 <script setup> 中访问注入的 class
- 使用 自定义注入名称 的
<style module>, useCssModule 接收一个匹配的 module attribute 值作为第一个参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| <script setup>
import { h, useCssModule } from 'vue';
const style = useCssModule();
const classes = useCssModule('classes');
</script>
|
CSS 中的 v-bind()
单文件组件的 <style> 标签支持使用 v-bind CSS 函数将 CSS 的值链接到动态的组件状态
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <template>
<div class="text">hello world</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return { color: 'red' };
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.text {
color: v-bind(color);
}
</style>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <template>
<p>hello world</p>
</template>
<script setup>
const theme = {
color: 'red',
};
</script>
<style scope>
p {
color: v-bind('theme.color');
}
</style>
|
进阶 API
渲染函数
- 如果组件定义了 setup 并且返回值是一个函数, 则其返回值作为该组件的渲染函数
- 如果组件定义了 render, 则将其作为渲染函数
- 如果组件定义了 template, 则将其作为模板进行编译成可执行的渲染函数
- 如果以上条件都不满足, 则使用容器的 innerHTML 作为模板
h()
当创建组件的 vnode 时, 子节点必须以 插槽函数 的形式传递, 如果组件只有默认插槽, 可以使用单个 插槽函数 传递, 否则, 必须以 插槽函数 的对象形式传递
创建虚拟 DOM 节点(vnode)
- 第一个参数是一个字符串(用于原生元素)或者一个 Vue 组件定义
- 第二个参数是要传入的 prop, 如果 插槽函数 不是对象形式时, 可以省略此参数
- 第三个参数是子节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| <script setup>
import { h } from 'vue';
h(
'div',
{
class: 'bar',
style: { color: 'red' },
innerHtml: 'hello',
onClick: () => {},
},
['hello world', h('span', 'gg')]
);
</script>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <script setup>
import { h } from 'vue';
import Foo from './Foo.vue';
h(Foo, {
someProp: 'hello world',
onUpdate: () => {},
});
h(Foo, () => 'default slot');
h(MyComponent, null, {
default: () => 'default slot',
header: () => h('div', 'hello div'),
footer: () => [h('span', 'one'), h('span', 'two')],
});
</script>
|
mergeProps()
class, style 将被合并成一个对象, onXxx 将被合并成一个数组
合并多个 props 对象, 用于处理含有特定的 props 参数的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| <script setup>
import { h, mergeProps } from 'vue';
const one = {
class: 'foo',
onClick: handlerA,
};
const two = {
class: { bar: true },
onClick: handlerB,
};
const merged = mergeProps(one, two);
</script>
|
cloneVNode()
克隆一个 vnode, 可在原有的基础上添加一些额外的 prop
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <script setup>
import { h, cloneVNode } from 'vue';
const original = h('div');
const cloned = cloneVNode(original, { id: 'foo' });
</script>
|
isVNode()
判断一个值是否为 vnode 类型
resolveComponent()
resolveComponent() 只能在 渲染函数 或 setup() 中使用
如果可以直接引入组件就不需要使用此方法
按名称手动解析已注册的组件, 未找到则抛出一个运行时警告并返回组件名字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <script setup>
import { h, resolveComponent } from 'vue';
const ButtonComponent = resolveComponent('ButtonComponent');
return () => h(ButtonComponent);
</script>
|
resolveDirective() 只能在 渲染函数 或 setup() 中使用
如果可以直接引入组件就不需要使用此方法
按名称手动解析已注册的指令, 未找到则抛出一个运行时警告并返回 undefined
1
2
3
4
5
| <script setup>
import { resolveDirective } from 'vue';
const myDirective = resolveDirective('myDirective');
</script>
|
用于给 vnode 增加自定义指令
- 第一个参数为要添加指令的 vnode
- 第二个参数为自定义指令数组, 每个自定义指令表示为
[directive, value, argument, modifiers] 形式的数组
- [directive] 指令本身
- [directive, value] 上述内容, 指令的值
- [directive, value, arg] 上述内容, 一个 String 参数,eg: v-on:click 中的 click
- [directive, value, arg, modifiers] 上述内容, 定义任意修饰符的 key:value 键值对
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <script setup>
import { h, withDirectives } from 'vue';
const pin = {
created() {
console.log('pin directive created...');
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('pin directive beforeMount...');
},
mounted(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {
console.log(binding.value, binding.arg, binding.modifiers);
el.style.fontSize = '20px';
el.style.color = '#08f';
},
};
return () =>
withDirectives(h('div', 'hello withDirectives'), [
[pin, 200, 'top', { animate: true }],
]);
</script>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { withDirectives, resolveDirective } from 'vue';
const foo = resolveDirective('foo');
const bar = resolveDirective('bar');
return withDirectives(h('div'), [
[foo, this.x],
[bar, this.y],
]);
|
withModifiers()
用于向事件处理函数添加内置 v-on 修饰符
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <script setup>
import { h, withModifiers } from 'vue';
const clk = function (e) {
console.log(e);
};
return () =>
h(
'button',
{
onClick: withModifiers(
(e) => {
console.log(e);
},
['stop', 'prevent']
),
},
'Click Me'
);
</script>
|
综合使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
| import {
createApp,
h,
ref,
defineComponent,
resolveComponent,
resolveDirective,
withDirectives,
withModifiers,
useSlots,
} from 'vue';
const HelloWorld = defineComponent((props, ctx) => {
const slots = useSlots();
const message = ref('This from hello world component');
const fooV = ref(250);
const show = ref(true);
const changeFooDirective = function () {
fooV.value = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 100);
show.value = fooV.value % 2 === 0 ? true : false;
};
const foo = resolveDirective('foo');
return () =>
h('div', [
h('p', slots?.header?.()),
h(
'p',
slots?.default?.({
message: message.value,
age: props.age > 0 ? props.age : 18,
})
),
show.value
? withDirectives(
h(
'p',
withDirectives(
h('span', [
'v-foo:bar1.uppercase=' + fooV.value,
h('br'),
'v-foo:bar2.uppercase=' + fooV.value
]),
[
[foo, fooV.value, 'bar1', { uppercase: true }],
[foo, fooV.value, 'bar2', { uppercase: true }]
]
)
),
[[foo, fooV.value, 'bar1', { uppercase: true }]]
)
: '',
h(
'p',
h(
'button',
{ onClick: changeFooDirective },
'Change v-foo value - ' + props.age
)
),
]);
}, {
props: ['name', 'age'],
directives: {
foo: {
created(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {
console.log('directives foo hooks created trigger... ', binding);
},
unmounted(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {
console.log('directives foo hooks unmounted trigger... ', binding);
},
},
},
}
);
const app = createApp({
setup(props, ctx) {
const gg = {
created(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {
console.log('withDirectives gg hooks created trigger... ', binding);
},
unmounted(el, binding, vnode, prevVnode) {
console.log('withDirectives gg hooks unmounted trigger... ', binding);
},
};
const HelloWorld = resolveComponent('hello-world');
return () => [
withDirectives(
h(
HelloWorld,
{ name: 'from createApp', age: -1 },
{
default: (slotScope) => `${slotScope.message} - ${slotScope.age} , This from createApp content`,
header: () => 'This from createApp by header slot...',
}
),
[[gg, 1000, 'bottom', { animate: true }]]
),
h('p', null, {
header: () => 'createApp use h 传递 header slot',
default: () => 'createApp use h 传递 default slot'
}),
h(
'button',
{ onClick: withModifiers((e) => alert('createApp withModifiers'), ['stop', 'prevent']) },
'Click Me withModifiers'
),
];
},
});
app.component('hello-world', HelloWorld);
app.mount('#app');
|
![vue3-directives-hooks-1]()
![vue3-directives-hooks-2]()
![vue3-directives-hooks-3]()
服务端渲染
renderToString()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
- 传入第二个可选的上下文对象用来在渲染过程中记录额外的数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import { createSSRApp } from 'vue';
import { renderToString } from 'vue/server-renderer';
const app = createSSRApp({
data() {
return { name: 'hello world' };
},
template: `<div>{{name}}</div>`,
});
const ctx = {};
(async () => {
const html = await renderToString(app, ctx);
console.log(html);
})();
|
renderToNodeStream()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
将输入渲染为一个 Node.js Readable Stream 实例
1
2
3
4
5
| import { renderToNodeStream } from 'vue/server-renderer';
const stream = renderToNodeStream(app);
stream.pip(res);
|
pipeToNodeWritable()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
将输入渲染并 pipe 到一个 Node.js Writable Stream 实例
1
2
3
4
| import { pipeToNodeWritable } from 'vue/server-renderer';
pipeToNodeWritable(app, {}, res);
|
renderToWebStream()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
将输入渲染为一个 Web ReadableStream 实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { renderToWebStream } from 'vue/server-renderer';
(async () => {
const res = new Response(renderToWebStream(app));
console.log(res);
console.log(await res.text());
})();
|
pipeToWebWritable()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
将输入渲染并 pipe 到一个 Web WritableStream 实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| import { pipeToWebWritable } from 'vue/server-renderer';
(async () => {
const tfs = new TransformStream();
pipeToWebWritable(app, {}, tfs.writable);
const res = new Response(tfs.readable);
console.log('pipeToWebWritable ', res);
console.log('pipeToWebWritable ', await res.text());
})();
|
renderToSimpleStream()
导出自 vue/server-renderer
通过一个简单的接口, 将输入以 stream 模式进行渲染
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| import { renderToSimpleStream } from 'vue/server-renderer';
let res = '';
renderToSimpleStream(
app,
{},
{
push(chunk) {
if (chunk == null) {
console.log('renderToSimpleStream render complete: ', res);
} else {
res += chunk;
}
},
destroy(err) {
console.log(err);
},
}
);
|
useSSRContext()
运行时 API, 用于获取传递给 renderToString 或者其他服务端渲染 API 的上下文对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| <script setup>
import { useSSRContext } from 'vue';
if(import.meta.env.SSR){
const ctx = useSSRContext();
}
</script>
|
data-allow-mismatch
Vue 3.5 支持
激活不匹配 预渲染的 HTML 的 DOM 结构不符合客户端应用的期望, 当 Vue 遇到激活不匹配时, 将尝试自动恢复并调整预渲染的 DOM 结构以匹配客户端的状态, 这将导致一些渲染性能的损失.
- 组件模板中存在不符合规范的 HTML 结构, eg: <p><div></div></p>
- 渲染所用的数据中包含随机生成的值, 由于同一个应用会在服务端和客户端执行两次, 每次执行生成的随机数都不能保证相同
- 服务端和客户端的时区不一致
可以消除激活不匹配警告的特殊的 attribute, 如果没有提供值, 则会允许所有类型的不匹配.
允许的值
- text
- children
- class
- style
- attribute
1
| <div data-allow-mismatch="text">{{ data.toLocaleString() }}</div>
|
工具类型
PropType<T>
用于在用运行时 props 声明时给一个 prop 标注更复杂的类型定义
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| import type { PropType } from 'vue';
interface Book{
title: string,
author: string,
year: number
}
export default {
props: {
book: {
type: Object as PropType<Book>,
required: true,
}
}
}
|
ComponentCustomProperties
用于增强组件实例类型以支持自定义全局属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import axios from 'axios';
declare module 'vue'{
interface ComponentCustomProperties {
$http: typeof axios
$translate: (key: string) => string
}
}
|
ComponentCustomOptions
用来扩展组件选项类型以支持自定义选项
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| import {Route} from 'vue-router';
declare module 'vue' {
interface ComponentCustomOptions {
beforeRouteEnter?(to: any, from: any, next: () => void): void
}
}
|
ComponentCustomProps
用于扩展全局可用的 TSX props, 以便在 TSX 元素上使用没有在组件选项上定义过的 props
1
2
3
4
5
6
| declare module 'vue'{
interface ComponentCustomProps {
hello?: string
}
}
export {}
|
CSSProperties
用于扩展在样式属性绑定上允许的值的类型
1
2
3
4
5
| declare module 'vue' {
interface CSSProperties {
[key: `--${string}`]: string
}
}
|
自定义渲染
createRenderer()
创建一个自定义渲染器, 可以在非 DOM 环境中使用 Vue 核心运行时的特性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import { createRenderer } from '@vue/runtime-core';
const { render, createApp } = createRenderer({
patchProp,
insert,
remove,
createElement,
});
export { render, createApp };
export * from '@vue/runtime-core';
|
Router
useLink
useRoute 返回当前的路由地址, 相当于模板中使用 $route
useRouter 返回路由器实例, 相当于模板中使用 $router
路由组件传参, 使用 props 将路由和组件解耦
- 布尔模式:
{path: '/users/:id', component: User, props: true}
- 命名视图:
{path: '/users/:id', components: {default: User, sidebar: SideBar}, props: {default: true, sidebar: true}}
- 对象模式:
{path: '/users/profile', component: User, props: {newsLetterPopup: false}}
- 函数模式:
{path: '/search', component: Search, props: (route) => ({query: route.query})}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
const User = { template: '<div>User {{$route.params.id}}</div>' };
const routes = [{ path: '/users/:id', component: User }];
const User = { props: ['id'], template: '<div>User {{id}}</div>' };
const routes = [{ path: '/users/:id', component: User, props: true }];
|
- beforeEnter 路由独享的守卫, 只在进入路由时触发, 不会在 params, query, hash 改变时触发
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| const routes = [
{
path: '/users/:id',
component: User,
beforeEnter: (to, from) => {
return false;
},
},
];
|
- onBeforeRouteUpdate 组合式 API 中使用组件 update 守卫
- onBeforeRouteLeave 组合式 API 中使用组件 leave 守卫
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| <script>
import { ref } from 'vue';
import { onBeforeRouteUpdate, onBeforeRouteLeave } from 'vue-router';
const userData = ref();
onBeforeRouteLeave((to, from) => {
const answer = window.confirm('leave?');
if (!answer) return false;
});
onBeforeRouteUpdate(async (to, from) => {
if (to.params.id != from.params.id) {
userData.value = await fetchUser(to.params.id);
}
});
</script>
|
编程式导航
- 当同时提供了 path, params 参数时, params 会被忽略
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import { useRouter } from 'vue-router';
const router = useRouter();
router.push({ path: '/user', params: { username: 'zhangsan' } });
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { username: 'zhangsan' } });
|
1
2
3
| router.push({ path: '/home', replace: true });
router.replace({ path: '/home' });
|
Pinia
store 是一个用 reactive 包装的对象, 不需要使用 .value 访问, 使用解构的方式将会丢失响应性
- defineStore 创建 store, 可使用 Option 对象 或 Setup 函数
- storeToRefs() 从 store 中提取属性时保持其响应性, 并且跳过所有的 action 或非响应式(不是 ref 或 reactive)的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| import { createApp, ref } from 'vue';
import { createPinia, defineStore, storeToRefs } from 'pinia';
const pinia = createPinia();
const app = createApp({});
app.use(pinia);
app.mount('#app');
const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', () => {
const count = ref(1);
const doubleCount = count.value * 2;
const increment = function () {
count.value++;
};
return { count };
});
const counter = useCounterStore();
const { count, doubleCount } = storeToRefs(counter);
const { increment } = counter;
|
- store.$dispose() 停止 store 的相关作用域, 并从 store 注册表中删除它. 插件可以覆盖此方法来清理已添加的任何副作用函数
- store.$reset() 重置 state 为初始值
- 使用 选项式 API 创建的 store 调用此方法, 使用 setup 创建的 store 调用此方法报错
Error: ... is built using the setup syntax and does not implement $reset()
- store.$patch() 批量修改 state, 可接收一个对象或者一个函数, 如果参数为函数, 函数接收一个参数 state 表示当前 store
- store.$subscribe() 订阅 state, 侦听 state 及其变化在 patch 后只触发一次,
默认情况下, state 订阅器被绑定在使用的组件上, 当组件卸载时, 它们将被自动移除, 如果想在组件卸载时仍保留它们, 传入第二个参数 { detached: true }, 将订阅器从组件中分离
- store.$onAction() 订阅 action, 传递给它的回调函数会在 action 本身之前执行,
默认情况下, action 订阅器被绑定在使用的组件上, 当组件卸载时, 它们将被自动移除, 如果想在组件卸载时仍保留它们, 传入第二个参数 true, 将订阅器从组件中分离
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| import { useCounterStore } from './useCounterStore.js';
const counter = useCounterStore();
const unsubscribe = counter.$onAction(
({ name, store, args, after, onError }) => {
after((result) => {});
onError((error) => {});
},
true
);
unsubscribe();
|
- setMapStoreSuffix() 修改 pinia 为每个 store 的 id 后面加上后缀, 默认 ‘Store’, 修改后会影响调用辅助函数 mapStores 后的 store 的访问方式
- mapStores() 将整个 store 映射为组件的计算属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import { mapStores } from 'pinia';
import { useCounterStore } from './useCounterStore.js';
import { useUserStore } from './useUserStore.js';
export default {
setup() {},
computed: {
...mapStores(useCounterStore, useUserStore),
},
methods: {
m1() {
console.log(this.counterStore.count);
this.counterStore.increment();
},
},
};
|
- mapState() 辅助函数, 将 state 属性映射为只读的计算属性
- mapWritableState() 辅助函数, 将 state 映射为可修改的属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import { mapState } from 'pinia';
import { useCounterStore } from './useCounterStore.js';
export default {
setup() {},
computed: {
...mapState(useCounterStore, ['count']),
...mapState(useCounterStore, {
myCount: 'count',
double: (store) => store.count * 2,
}),
},
};
|
- mapActions() 辅助函数, 将 action 属性映射为组件的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import { mapActions } from 'pinia';
import { useCounterStore } from './useCounterStore.js';
export default {
setup() {},
methods: {
...mapActions(useCounterStore, {
myIncrement: 'increment',
}),
},
};
|