Redis
Remote Dictionary Server 即远程字典服务, 是一个开源的使用 ANSI C 语言编写、支持网络、可基于内存亦可持久化的日志型、Key-Value 数据库,并提供多种语言的 API, Redis 能读的速度是 11 万次/s,写的速度是 8.1 万次/s
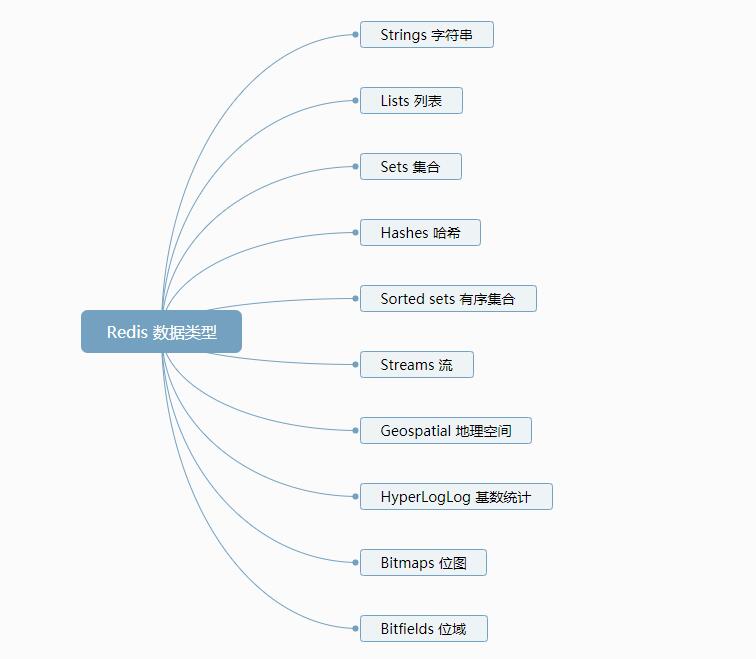
Redis 通常被称为数据结构服务器, 因为它的核心数据类型包括字符串、列表、字典(或哈希)、集合和排序集合等大多编程语言都支持的数据类型. 高版本版的 Redis 还添加了计算基数、地理定位和流处理等高级功能
数据类型
工具命令
- redis-benchmark 压测工具
- -h 主机名
- -p 端口号
- -s socket 连接(覆盖 host 和 port)
- -a 认证密码
- --user 用户名
- -c 客户端并发连接数(default 50)
- -n 请求数(default 100000)
- -d 测试数据的大小(default 3)
- --dbnum 连接的数据库编号(default 0)
- -k 是否保持连接
- -r SET/GET/INCR 使用随机 key, SADD 使用随机值
- -p 通过管道传输
- -q 退出, 仅显示 query/sec 值
- --csv 以 CSV 格式输出
- -l 循环永远运行测试
- -t 仅运行以逗号分割的命令列表
- -I Idle 模式, 仅打开 N 个 idle 连接并等待
- -x 从 STDIN 读取最后一个参数
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379>redis-benchmark -h localhost -p 6379 -c 100 -n 100000 -d 10 -t set,get,hset,hget,lpush,rpush,sadd |
redis-check-aof 检查 aof 备份文件
redis-check-rdb 检查 rdb 备份文件
redis-cli –user <username> –pass <password> 使用用户名密码连接 redis
- -r 指定运行命令的次数
- -i 设置不同命令调用之间的延迟(以秒为单位)
- -x 从标准输入中读取最后一个参数
- --bigkeys 查找大键
- --stat 监控当前 redis 的使用情况
- --eval <file> 使用 EVAL 命令解析 lua 脚本
- --function-rdb <filename> 从现有服务器中提取函数(不包含 key)
1 | # 加载 lua 脚本注册的 redis 函数 |
开机启动
- 创建
/usr/lib/systemd/system/redis.service服务文件, 使用yum install安装 Redis 自动创建此文件 - 编辑
redis.service文件
1 | [Unit] # 控制单元定义 |
- 使用命令
systemctl daemon-reload重启系统服务管理守护进程 - 使用命令
systemctl start redis.service启动 Redis 服务 - 使用命令
systemctl enable redis.service允许 Redis 服务开机启动
CONFIG 命令
CONFIG GET parameter [parameter…] 获取指定配置项的值
CONFIG HELP 显示 CONFIG 命令的帮助信息
CONFIG RESETSTAT 重置 INFO 返回的统计信息, ok 成功
CONFIG REWRITE 将内存中的配置项重写到配置文件中
CONFIG SET parameter value [parameter value …] 设置配置项
INFO [section [section …]] 返回服务的相关信息, 没有参数返回所有
server 返回 redis 服务的通用信息
clients 返回客户端链接的信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9# Clients
connected_clients:1
cluster_connections:0
maxclients:10000
client_recent_max_input_buffer:20480
client_recent_max_output_buffer:0
blocked_clients:0
tracking_clients:0
clients_in_timeout_table:0memory 返回内存的信息
persistence 返回持久化的信息 RDB 和 AOF
stats 返回统计信息
replication 返回副本的信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:5b0d7d50614d939be22b4bedb80450d13bfd64a0
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:0
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0cpu 返回 cpu 的信息
commandstats 返回命令统计信息
latencystats 返回命令延迟百分比统计信息
cluster 返回集群信息
modules 返回模块信息
keyspace 返回数据库相关统计信息
1
2# Keyspace
db0:keys=3,expires=0,avg_ttl=0errorstats 返回错误统计信息
all 返回所有信息(除了 modules)
default 返回默认配置信息
everything 返回所有信息(包含 all 和 modules)
help command 显示命令的帮助信息
- @[string] 显示当前数据类型的帮助信息
ECHO message 打印信息
SAVE 保存数据到本地磁盘
WAIT numreplicas timeout 阻止当前客户端, 直到所有先前的写入命令成功传输并至少由指定数量的副本确认, 如果达到了以毫秒为单位指定的超时, 则即使尚未达到指定的副本数量, 该命令也会返回
ROLE 返回当前实例的角色是 master、slave、sentinel, 和当前实例上下文副本的信息
PING [message] 测试连接是否正常, 通常返回 PONG, 如果传入了 message 则会输出 message
QUIT 关闭退出当前连接
SHUTDOWN [NOSAVE|SAVE] [NOW] [FORCE] [ABORT] 同步保存数据到硬盘上并关闭服务
MONITOR 启动监听模式输出服务器执行的每条命令
clear 清空屏幕
Keys 命令
操作 key
TYPE key 返回指定 key 的类型, none 表示 key 不存在
EXISTS key [key …] 检查指定 key 是否存在, 1 存在, 0 不存在
KEYS pattern 查找给定模式(pattern)的 key, 返回列表, 未找到返回 (empty array),
KEYS *返回所有 keyDEL key [key…] 阻塞删除 key 并返回成功删除 key 的数量
UNLINK key [key …] 非阻塞从键空间中取消指定 key 的链接(在其他线程中执行实际的内存回收), 并返回成功取消 key 的数量, 如果 key 不存在则忽略
RENAME key newKey 修改 key 的名称, 如果指定 key 不存在返回 错误, 如果 newkey 已存在则覆盖
RENAMENX key newkey 修改 key 的名称, 如果指定 key 不存在返回 错误, 如果 newkey 已存在不执行任何操作返回 0, 否则返回 1
MOVE key db 将当前数据库中的 key 移动到指定的数据库(db)中
DUMP key 序列化指定 key, 并返回被序列化的值, 不存在返回 <nil>
TOUCH key [key …] 更改指定 key 的最后一次访问时间并返回修改成功的数量, 如果 key 不存在则忽略
SORT key [BY pattern] [LIMIT offset count] [GET pattern [GET pattern …]] [ASC|DESC] [ALPHA] [STORE destination]
对 list、set、zset 集合中的元素进行排序, 默认是按照数字或者元素的双精度浮点数去比较
SCAN cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] [TYPE type] 查找给定模式(pattern)的 key, 返回列表和上次遍历时的游标
- COUNT 控制匹配结果的数量, 默认为 10
- TYPE 过滤匹配结果中的类型, 可取值 string, list, set 等 redis 支持的数据类型
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS * |
过期时间
设置过期时间
- EXPIRE key seconds [NX|XX|GT|LT] 为指定 key 设置过期时间(单位秒), 1 设置成功, 0 指定 key 不存在或者提供的参数跳过了操作
- EXPIREAT key unix-time-seconds [NX|XX|GT|LT] 为指定 key 设置过期使用 unix 时间戳, 1 设置成功, 0 指定 key 不存在或者提供的参数跳过了操作
- PEXPIRE key milliseconds [NX|XX|GT|LT] 为指定 key 设置过期时间(单位毫秒), 1 设置成功, 0 指定 key 不存在或者提供的参数跳过了操作
- PEXPIREAT key unix-time-milliseconds [NX|XX|GT|LT] 为指定 key 设置过期时间使用 unix 时间戳, 1 设置成功, 0 指定 key 不存在或者提供的参数跳过了操作
- EXPIRETIME key 返回指定 key 将过期的绝对 Unix 时间戳(以秒为单位), -1 表示 key 存在但没有过期时间, -2 表示 key 不存在, Redis 7.0 支持
- PEXPIRETIME key 返回指定 key 将过期的绝对 Unix 时间戳(以毫秒为单位), -1 表示 key 存在但没有过期时间, -2 表示 key 不存在, Redis 7.0 支持
- NX 以上命令该参数作用相同, 仅当指定 key 没有过期时间时
- XX 以上命令该参数作用相同, 仅当指定 key 存在过期时间时
- GT 以上命令该参数作用相同, 仅当新的过期时间大于当前的过期时间
- LT 以上命令该参数作用相同, 仅当新的过期时间小于当前的过期时间
获取过期时间
- TTL key 返回指定 key 以秒为单位剩余的生存时间
- PTTL key 返回指定 key 以毫秒为单位剩余的生存时间
- -2 key 不存在
- -1 key 存在但没有设置剩余生存时间
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> TTL age |
取消过期时间
- PERSIST key 移除指定 key 的过期时间, key 将永久保持, 1 成功, 0 key 不存在或者未设置过期时间
数据库操作
- RANDOMKEY 从当前数据库随机返回一个 key, 如果当前数据库为空则返回 <nil>
- SWAPDB index1 index2 切换两个数据库
- SELECT index 更改当前连接的选定的数据库
- DBSIZE 返回当前数据库中 key 的数量
清空数据库
- FLUSHALL [ASYNC|SYNC] 清除所有数据库中的 key, 执行成功返回 ok
- FLUSHDB [ASYNC|SYNC] 清除当前数据库中的 key, 执行成功返回 ok
副本
- REPLICAOF host port 将当前服务器设置为指定主机端口上服务器的副本, 通常返回 ok, Redis 5.0 开始代替
SLAVEOF- 如果当前服务器已经是某个服务器的副本, 则取消对旧服务器的连接同步, 并开始对新服务器同步, 丢弃旧有数据集
- NO ONE 如果当前服务器已经是副本, 此参数将当前服务器变为 master, 并停止与主服务器的连接同步
安全认证
- AUTH [username] password 对当前连接的认证, 或者切换用户
配置文件配置项
include /path/to/*.conf # 导入其他 redis 配置文件
protected-mode yes # 保护模式, 默认 yes, 只能允许本机连接
tcp-backlog 511 # tcp 连接数
timeout 0 # 关闭客户端连接的延迟, 0 表示禁用, 单位秒
tcp-keepalive 300 # 保持长连接的时间, 单位秒
TLS/SSL
安全连接配置项, 默认未开启
- tls-port 6379 # 安全连接端口
- tls-cert-file redis.cert # 安全连接证书
- tls-key-file redis.key # 安全连接 key
- tls-key-file-pass secret # key 文件加密摘要
- tls-client-cert-file client.crt # 客户端安全连接证书
- tls-client-key-file client.key # 客户端安全连接 key
- tls-client-key-file-pass secret # 客户端安全连接 key 文件加密摘要
- tls-ca-cert-file ca.crt # CA 证书
- tls-ca-cert-dir /etc/ssl/certs # CA 证书目录
- tls-auth-clients no # no 不需要也不接受客户端证书连接, optional 证书不必需, 如果提供证书则必须验证有效
- tls-session-caching no # 默认启用 TLS 会话缓存, no 表示禁用缓存
- tls-session-cache-size 5000 # TLS 缓存大小, 默认 20480
- tls-session-cache-timeout 60 # TLS 缓存有效期, 默认 300 秒
通用设置
loglevel notice # 设置日志级别, 默认 notice
- debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
- verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
- notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
- warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
syslog-enabled no # 是否允许指向 系统 日志
syslog-ident redis # 日志标识符
databases 16 # 默认数据库数量
always-show-logo no # 是否总是显示 logo
set-proc-title yes # 设置进程标题
MEMORY
- maxmemory-policy noeviction # 内存管理策略
- volatile-lru 使用 LRU 算法移除 key, 只对设置了过期时间的 key
- allkeys-lru 在所有集合 key 中, 使用 LRU 算法移除 key
- volatile-lfu 使用 LFU 算法移除 key, 只对设置了过期时间的 key
- allkeys-lfu 在所有集合 key 中, 使用 LFU 算法移除 key
- volatile-random 在过期集合 key 中, 移除随机的 key, 只对设置了过期时间的 key
- allkeys-random 在所有集合 key 中, 移除随机的 key
- volatile-ttl 移除那些 TTL 值最小的 key, 即那些最近要过期的 key
- noeviction 不进行移除, 针对写操作, 只是返回错误信息
- maxmemory-samples 5 # 设置 Redis 移除 key 时的样本数量, 10 接近 LRU 算法但非常消耗内存, 3 最快却不是精确的
SNAPSHOTTING
- save 3600 1 300 100 60 10000 # 快照执行机制, 3600 秒后如果超过 1 次更改, 300 秒后超过 100 次更改, 60 秒后超过 10000 次更改
1 | save <seconds> <changes> [<seconds> <changes> ...] |
- stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes # 是否开启停止在保存快照发生错误的时的写操作
- rdbcompression yes # 开启 rdb 文件压缩
- rdbchecksum yes # 开启 rdb 文件的校验检查
SECURITY
- acllog-max-len 128 # ACL 日志在内存中时的最大条目数
- aclfile /etc/redis/users.acl # 默认 ACL 配置文件
- io-threads 4 # I/O 线程
Redis Pipelining
当客户端使用流水线发送命令时, 服务器将被迫使用内存对回复进行排队. 因此, 如果需要使用流水线发送大量命令时最好尽量等分分批发送命令
Redis 流水线是一种通过一次发出多个命令而无需等待每个命令的响应来提高性能的技术, 大多数 Redis 客户端都支持流水线.
1 | # 使用 netcat 命令测试 |
Redis 编程
Redis 函数
Redis 7.0 支持
Redis 函数是临时脚本的进化步骤, 函数提供与脚本相同的核心功能但却是数据库的一流软件工件
Redis 将函数作为数据库的一个组成部分进行管理, 并通过数据持久化和复制确保它们的可用性. 由于函数是数据库的一部分, 因此在使用前声明, 因此应用程序不需要在运行时加载它们, 也不必冒事务中止的风险. 使用函数的应用程序仅依赖于它们的 API, 而不依赖于数据库中的嵌入式脚本逻辑
Redis 函数可以将 Lua 的所有可用功能用于临时脚本, 唯一例外的是 Redis Lua 脚本调试器
Redis 函数还通过启用代码共享来简化开发, 每个函数都属于一个库, 任何给定的库都可以包含多个函数, 库的内容是不可变的, 并且不允许对其功能进行选择性更新. 取而代之的是, 库作为一个整体进行更新, 在一个操作中将它们的所有功能一起更新. 这允许从同一库中的其他函数调用函数, 或者通过使用库内部方法中的公共代码在函数之间共享代码, 这些函数也可以采用语言本机参数
Redis 函数也被持久化到 AOF 文件中, 并从主服务器复制到副本服务器, 因此它们与数据一样可以持久化
Redis 函数的执行是原子的, 函数的执行在其整个时间内阻止所有服务器活动, 类似于事务的语义, 已执行函数的阻塞语义始终适用于所有连接的客户端, 因为运行一个函数会阻塞 Redis 服务器
- 函数都属于一个库, 任何给定的库都可以包含多个函数
- 库的内容是不可变的, 并且不允许选择性地更新其函数, 只能将库作为一个整体进行更新
函数命令
- FUNCTION help 显示 FUNCTION 的帮助信息
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> FUNCTION help |
- FUNCTION DELETE 删除指定的库
- FUNCTION LIST 查看所有库和函数
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> FUNCTION LIST |
- 加载库和函数
每个 Redis 函数都属于一个加载到 Redis 的库, 使用命令 FUNCTION LOAD 将库加载到数据库, 库必须以 shebang 语句开头 #!<engine name> name=<library name>
1 | # 加载一个空库 |
注册调用
注册
- redis.register_function(name, callback, flags, description) 注册函数
- name 注册的函数名
- callback 注册的函数
- flags
- no-writes 标识脚本只能读取但不能写入
- allow-oom 标识允许脚本在服务器内存不足(OOM)时执行
- allow-stable
- no-cluster 标识脚本在 Redis 集群模式下返回错误, 防止对集群中的节点执行脚本
- allow-cross-slot-keys 允许脚本从多个 slot 访问密钥
- description 函数描述
调用
- FCALL function numkeys [key [key …]] [arg [arg …]] 调用注册的函数
- FCALL_RO function numkeys [key [key …]] [arg [arg …]] 调用注册的只读函数
Redis 命令行注册调用
1 | # 方式1 |
Lua 脚本文件注册调用
1 | #!lua name=mylib |
1 | [root@centos7 workspace]# cat mylib.lua | redis-cli -x FUNCTION LOAD REPLACE |
Lua 脚本
Redis 允许在服务器上上传和执行 Lua 脚本, 脚本可以采用编程控制结构并在执行时使用大部分命令来访问数据库, 因为脚本在服务器中执行, 所以从脚本中读取和写入数据非常高效.
Redis 保证脚本的原子执行, 在执行脚本时, 所有服务器活动在其整个运行期间都被阻止.
Lua 允许在 Redis 中运行部分应用程序逻辑, 这样的脚本可以跨多个键执行条件更新, 可能以原子方式组合几种不同的数据类型
Lua 脚本由嵌入式执行引擎在 Redis 中执行, 尽管服务器执行它们, 但 EVAL 脚本被视为客户端应用程序的一部分, 这就是它们没有命名、版本化或持久化的原因. 因此, 如果所有脚本丢失, 应用程序可能需要随时重新加载
脚本命令
脚本参数化 为了确保在独立部署和集群部署中正确执行脚本, 脚本访问的所有键名都必须作为输入键参数显式提供
EVAL script numkeys key [key …] arg [arg …] 执行 Lua 脚本
- script 要执行的脚本语句
- numkeys 指定后续的参数有几个 key
- key 要操作的键的数量, 在 Lua 脚本中通过
KEYS[1],KEYS[2]获取 - arg 参数, 在 Lua 脚本中通过
ARGV[1],ARGV[2]获取
EVALSHA sha1 numkeys key [key …] arg [arg …] 使用缓存 Lua 脚本的 sha 执行脚本(SCRIPT LOAD 命令缓存脚本)
EVAL_RO script numkeys [key [key …]] [arg [arg …]] 只读版本的 EVAL 命令, Redis 7.0 支持
EVALSHA_RO sha1 numkeys [key [key …]] [arg [arg …]] 只读版本的 EVALSHA 命令, Redis 7.0 支持
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return 10" 0 |
每次执行脚本都需要重新加载一遍脚本代码, 浪费资源, 使用 脚本缓存
lua 脚本中的 redis 实例
redis 单例实例, 使脚本能够与运行它的 Redis 服务器进行交互
全局变量
- KEYS 获取脚本声明的键参数
- ARGV 获取脚本声明的键参数剩余的参数
- redis.call(command [, arg…]) 执行 redis 命令并返回结果, 如果遇到错误时直接返回给客户端
- redis.pcall(command [, arg…]) 执行 redis 命令并返回结果, 如果遇到错误时将返回给脚本的执行上下文
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> GET name |
- redis.error_reply(x) 辅助函数, 返回一个错误信息
- redis.status_reply(x) 辅助函数, 可以修改 Redis 命令的默认返回值 OK
1 | # 返回错误信息 |
- redis.sha1hex(x) 返回单个字符串参数的 SHA1 十六进制摘要信息
- redis.log(level, message) 写入 Redis 服务器日志
- redis.LOG_DEBUG 日志级别
- redis.LOG_VERBOSE 日志级别
- redis.LOG_NOTICE 日志级别
- redis.LOG_WARNING 日志级别
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return redis.sha1hex('')" 0 |
redis.setresp(x) 设置执行脚本和服务器之间的请求应答协议, 默认值 2. Redis 6.0 支持
redis.set_repl(x)
redis.replicate_commands()
redis.breakpoint() 在使用 Redis Lua 调试器时触发断点
redis.debug(x) 在 Redis Lua 调试器控制台中打印其参数
redis.acl_check_cmd(command [,arg…]) 用于检查运行脚本的当前用户是否具有使用给定参数执行给定命令的 ACL 权限, 返回值布尔类型. Redis 7.0 支持
redis.register_function(name, callback, flags, description) Redis 7.0 支持
redis.REDIS_VERSION 以字符串形式返回当前 Redis 服务器版本, 格式 MM.mm.PP. Redis 7.0 支持
redis.REDIS_VERSION_NUM 以数字形式返回当前 Redis 服务器版本, 格式为十进制值. Redis 7.0 支持
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return redis.REDIS_VERSION" 0 |
脚本缓存
存储在服务器的脚本专用缓存中, 缓存内容由脚本的 SHA1 摘要作为缓存中的唯一标识
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> SCRIPT help # 脚本帮助命令 |
- SCRIPT FLUSH 从脚本缓存中移除所有脚本, 返回 ok
- SCRIPT KILL 杀死系统当前正在运行的 Lua 脚本(又名慢脚本)
- SCRIPT DEBUG 设置脚本内执行时的模式
- SCRIPT LOAD <script> 将脚本加载到服务器缓存中, 并不立即执行
1 | # 添加 Lua 缓存脚本 |
- SCRIPT EXISTS <script> [script …] 查看缓存中是否存在 sha 对应的脚本, 1 表示存在, 0 表示不存在
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> SCRIPT EXISTS d3c21d0c2b9ca22f82737626a27bcaf5d288f99f |
脚本复制
一般在集群部署环境下, Redis 确保脚本执行的所有写操作也被发送到副本以保持一致性, 脚本复制有两种概念
- 逐字复制: master 将脚本的源代码发送到 slave, 然后 slave 执行脚本并写入效果.
- 在短脚本生成许多命令的情况下, 可以节省资源, 但意味着 slave 会重做 master 完成的相同工作而浪费资源
- 效果复制: 仅复制脚本的数据修改命令, slave 然后执行命令而不执行任何脚本, 从 redis 5.0 开始为默认模式
脚本效果复制 —— 复制命令
在这种模式下,在执行 Lua 脚本的同时, Redis 会收集 Lua 脚本引擎执行的所有实际修改数据集的命令, 当脚本执行完成时, 脚本生成的命令序列被包装到一个 事务 中并发送到副本和 AOF
Lua API
- 使用未声明为本地的变量和函数会引起 Redis 的报错
- 沙盒执行上下文不支持使用导入的 Lua 模块
数据类型转换
RESP2
- RESP2 -> Lua
- RESP2 整数 -> Lua 数
- RESP2 批量字符串 -> Lua 字符串
- RESP2 数组 -> Lua 表(可能嵌套额其他 Redis 数据类型)
- RESP2 状态 -> 包含状态字符串的单个 ok 字段的 Lua 表
- RESP2 错误 -> 包含错误字符串的单个 err 字段的 Lua 表
- RESP 空批量|空多批量 -> Lua false 布尔类型
- Lua -> RESP2
- Lua 数字 -> RESP2 整数(数字转为整数, 舍去小数部分)
- Lua 字符串 -> RESP 批量字符串
- Lua 表(索引, 非关联数组) -> RESP2 数组(在表中遇到第一个 nil 时截断)
- 带有单个 ok 字段的 Lua 表 -> RESP2 状态
- 带有单个 err 字段的 Lua 表 -> RESP2 错误
- Lua false 布尔类型 -> RESP2 空批量
- Lua true 布尔类型 -> RESP2 整数 1
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return {1, 2, {3, 'hello world'}, 'bar'}" 0 |
RESP3
一旦 Redis 的回复采用 RESP3 协议, 所有 RESP2 到 Lua 的转换规则都适用, 并添加以下内容
- RESP3 -> Lua
- RESP3 map -> 带有单个映射字段的 Lua 表, 其中包含表示映射字段和值的 Lua 表
- RESP3 set -> 具有单个集合字段的 Lua 表
- RESP3 null -> Lua nil
- RESP3 true -> Lua true 布尔类型
- RESP3 false -> Lua false 布尔类型
- RESP3 浮点数 -> 带有一个浮点数字段的 Lua 表
- RESP3 大数字 -> 带有单个大数字字段的 Lua 表. Redis 7.0 支持
- RESP3 逐句逐字字符串 -> Lua 表, 其中包含单个 verbatim_string 字段的 Lua 表, 其中包含两个字段 string 和 format,分别表示 verbatim string 和它的格式. Redis 7.0 支持
- Lua -> RESP3
- Lua Boolean -> RESP3 Boolean
- 将单个映射字段设置为关联 Lua 表的 Lua 表 -> RESP3 map
- 将单个集合字段设置为关联 Lua 表的 Lua 表 -> RESP3 set, 值可以为任何值, 都会被丢弃
- 带有单个浮点数字段的 Lua 表到关联的 Lua 表 -> RESP3 浮点数
- Lua nil -> RESP3 null
外部库
struct
- struct.pack(x) 返回一个结构编码的字符串, 接收一个结构格式字符串作为第一个参数, 后面是要编码的值
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return struct.pack('bb', 1, 2)" 0 |
- struct.unpack(x) 返回结构的解码值, 接收一个结构格式字符串作为第一个参数, 然后是编码结构的字符串
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return {struct.unpack('BxxH', ARGV[1])}" 0 "\x01\x00\x00\x02\x00" |
- struct.size(x) 返回结构的大小(以字节为单位), 接收结构格式字符串作为唯一参数
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return struct.size('b')" 0 |
结构格式
- > 大端
- < 小端
- ![num] 结盟
- x 填充
- b/B 有/无符号字节
- h/H 有/无符号短
- l/L 有/无符号长
- T 大小
- i/In 大小为 n 的有/无符号整数(默认为 int 的大小)
- cn n 个字符的序列, 打包时, n ==0 表示整个字符串, 解包时, n == 0 表示使用先前读取的数字作为字符串的长度
- s 零终止字符串
- f float
- d double
- (space) 忽略
cjson
cjson 库提供了来自 Lua 的快速 JSON 编码和解码
- cjson.encode(x) 返回作为其参数提供的 Lua 数据类型的 JSON 编码字符串
- cjson.decode(x) 从作为其参数提供的 JSON 编码字符串返回 Lua 数据类型
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return cjson.encode({ 1, 2, 'foo', 'bar' })" 0 |
cmsgpack
cmsgpack 库提供了来自 Lua 的快速 MessagePack 编码和解码
- cmsgpack.pack(x) 返回作为参数给出的 Lua 数据类型的压缩字符串编码
- cmsgpack.unpack(x) 返回解码其输入字符串参数的解压缩值
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return cmsgpack.pack({'foo', 'bar', 'baz', 'hello'})" 0 |
bit
bit 提供对数字的按位运算
- bit.tobit(x)` 将数字格式化为位运算的数值范围并返回
- bit.tohex(x [, n]) 将第一个参数转换为十六进制并返回, 第二个参数的绝对值控制返回值的数量
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return bit.tobit(1)" 0 |
- bit.bnot(x) 返回其参数的按位非运算
- bit.bor(x1 [, x2…]) 返回其所有参数的按位或运算
- bit.band(x1 [, x2…]) 返回其所有参数的按位与运算
- bit.bxor(x1 [, x2…]) 返回其所有参数的按位异或运算
1 | # 0000 1100 12 |
- bit.lshift(x, n) 返回第一个参数按位左移 n 位的结果
- bit.rshift(x, n) 返回第一个参数按位右移 n 位的结果
- bit.arshift(x, n) 返回第一个参数按位算术右移 n 位的结果, 不改变符号位的移位操作
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return bit.lshift(1, 3)" 0 |
- bit.rol(x, n) 按第二个参数给定的位数返回其第一个参数的按位左旋转
- bit.ror(x, n) 按第二个参数给定的位数返回其第一个参数的按位右旋转
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return bit.rol(12, 1)" 0 |
- bit.bswap(x) 交换其参数的字节并返回它, 可用于将小端 32 位数字转换位大端 32 位数字, 反之亦然
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> EVAL "return bit.bswap(1)" 0 |
ACL
Redis 6.0 支持
ACL(access control list)访问控制列表的简称, 是为了控制某些 Redis 客户端在访问 Redis 服务器时, 能够执行的命令和能够获取的 key, 提高操作安全性, 避免对数据造成损坏
- ACL HELP 显示 ACL 的帮助信息
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> ACL HELP |
规则分类
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| on | 启用用户, 默认为 off |
| off | 禁用用户 |
| +<command> | 将命令添加到用户可以调用的命令列表中 |
| -<command> | 将命令从用户可以调用的命令列表中移除 |
| +<command>|subcmd | 允许使用已禁用命令的特定子命令 |
| +@<category> | 允许用户调用 category 类别中的所有命令, 可以使用 ACL CAT 命令查看所有类别 |
| -@<category> | 禁止用户调用 category 类别中的所有命令 |
| allcommands | +@all 的别名 |
| nocommands | -@all 的别名 |
| ~<pattern> | 允许用户可以访问的 key(正则匹配), 例如: ~foo:* 只允许访问 foo:* 的 key |
| %R~<pattern> | 添加指定的只读 key(正则匹配), 例如: %R~app:* 只允许读 app:* 的 key, Redis 7.0 支持 |
| %W~<pattern> | 添加指定的只写 key(正则匹配), 例如: %W~app:* 只允许写 app:* 的 key, Redis 7.0 支持 |
| %RW~<pattern> | 添加指定的可读可写的 key(正则匹配), 例如: %RW~app:* 只允许读写 app:* 的 key, Redis 7.0 支持 |
| allkeys | ~* 的别名 |
| resetkeys | 移除所有的 key 匹配模式 |
| &<pattern> | 允许用户可使用的 Pub/Sub 通道(正则匹配) |
| allchannels | &* 的别名 |
| resetchannels | 移除所有的通道匹配模式 |
| ><password> | 为用户添加明文密码, 服务器自动转换成 hash 存储, 例如: >123456 |
| <<password> | 从有效密码列表中删除密码 |
| #<hash> | 为用户添加 hash 密码, 例如: #cab3…c4f2 |
| !<hash> | 从有效密码列表中删除密码 |
| nopass | 删除所有与用户关联的密码 |
| resetpass | 刷新密码列表并删除 nopass 状态 |
- ACL CAT 显示 Redis 的所有分类
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> ACL CAT |
- ACL USERS 列出所有已配置用户名
- ACL WHOAMI 返回当前连接服务器的用户名, 默认 default
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> ACL WHOAMI |
ACL SAVE 将 ACLs 配置项从内存保存到 ACL 文件中
ACL DELUSER [username…] 删除指定的 ACL 用户, default 用户不能被删除
ACL SETUSER 设置用户访问权限
ACL GETUSER username 获取指定用户的权限
1 | # 添加 lisi 账号, 明文密码 123456, 添加所有分类的命令 |
- ACL LIST 显示 Redis 服务器当前活动的 ACL 规则
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> ACL LIST |
- ACL DRYRUN username command [arg [arg …]] 模拟指定用户对给定命令的执行, 此命令可以用来测试用户的权限而无需启用用户, Redis 7.0 支持
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> ACL DRYRUN zhangsan ZADD zs 1 hello 2 world 3 zs |
事务
=== Redis 单条命令是保证原子性的, 但是 Redis 事务不保证原子性 ===
=== Redis 事务没有隔离级别的概念 ===
所有的命令在事务中, 并没有被执行而是加入队列, 只有发起执行命令的时候才会执行! EXEC
Redis 事务允许在一个步骤中执行一组命令, 事务中的所有命令都是串行化的, 并按顺序执行. 在 Redis 事务执行过程中, 另一个客户端发送的请求将永远不会被处理. 这保证了命令作为一个单独的操作执行
Redis 事务执行的三个重要保证:
- 批量操作在发送 EXEC 命令前被放入队列缓存
- 收到 EXEC 命令后进入事务执行, 事务中任意命令执行失败, 其余的命令依然被执行
- 事务执行过程, 其他客户端提交的命令请求不会插入到事务执行命令序列中
事务开始到执行的三个阶段
- 开启事务(multi): 使用
MULTI命令标记从非事务状态切换到事务状态 - 命令入队: 命令不会被立即执行, 而是被放入一个事务队列
- 执行事务(exec)或丢弃(discard)
事务命令
MULTI 标记一个事务块的开启, 通常返回 ok
EXEC 执行事务, 通常返回 ok
- 必须在
MULTI命令之后才能调用, 否则报错 ERR EXEC without MULTI - 如果
WATCH观察的 key 在当前的事务执行时已被修改, 则返回 <nil>
- 必须在
DISCARD 丢弃事务, 通常返回 ok
- 必须在
MULTI命令之后才能调用, 否则报错 ERR DISCARD without MULTI
- 必须在
WATCH key [key …] 监视一个或多个 key, 如果在事务执行之前观察的 key 被修改, 则事务将被打断, 通常返回 ok
- 如果在
MULTI命令后调用, 则会报错 ERR WATCH inside MULTI is not allowed
- 如果在
UNWATCH 取消所有观察的 key, 通常返回 ok, 如果调用了
EXEC或DISCARD命令, 通常不再需要调用此命令
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> GET money |
编译时错误
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> SET key1 hello |
运行时错误
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> MULTI # 开启事务 |
不支持回滚
- Redis 命令只会因为错误的语法而失败(并且这些问题不能在入队时发现), 或是命令用在了错误类型的键上: 从实用性的角度来说, 失败的命令是由编程错误造成的, 而这些错误应该在开发环境中被发现, 不应该出现在生产环境中
- 因为不需要对回滚进行支持, 所有 Redis 的内部可以保持简单且快速
持久化
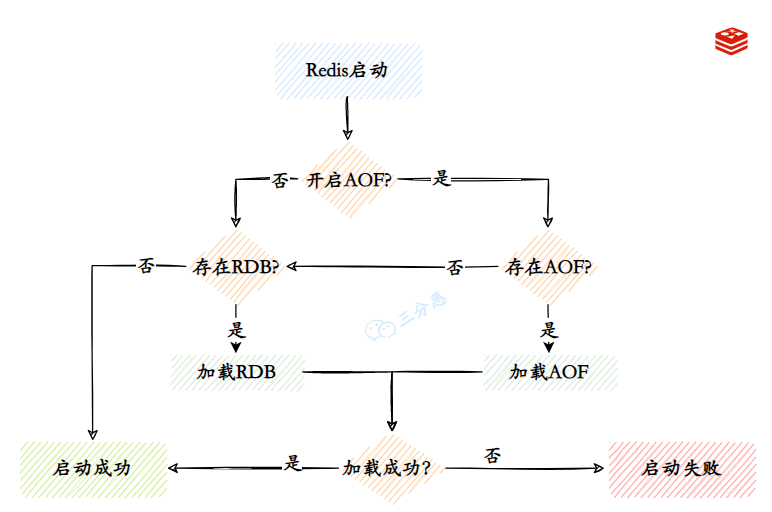
Redis 是基于内存的数据库, 遇到断电就会丢失数据, 持久化就是将内存中的数据保存到磁盘中便于以后使用, Redis 提供了 RDB 和 AOF 两种持久化方式, 默认使用 RDB 方式持久化数据
Redis 在持久化的过程中, 会先将数据写入到一个临时的文件中, 待持久化过程结束后, 才会用这个临时文件替换赏赐持久化生成的文件
触发方式
通过
FLUSHALL/FLUSHDB命令主动触发通过
SAVE/BGSAVE命令主动触发通过配置文件定期触发持久化操作
1 | # redis 7.0 写法 |
RDB
RDB(Redis Database), 在指定的时间间隔以指定的次数将内存中的数据集以快照的方式写入一个二进制文件中, 然后保存到磁盘中, 也就是 snapshot 快照, 默认生成的文件为 dump.rdb
Redis 会单独 fork 一个子进程进行持久化, 而主进程不会进行任何 I/O 操作, 这样就保证了 Redis 极高的性能, 如果需要进行大规模数据的恢复,且对于数据恢复的完整性不是非常敏感, 此方式比 AOF 方式更加的高效
dbfilename dump.rdb默认文件名dir ./默认存储目录redis-check-rdb 检查 RDB 文件
RDB 优点
- 每隔一段时间完全备份一次
- 容灾简单, 可远程传输
- RDB 最大限度地提高了 Redis 的性能
- 文件较大时重启和恢复速度要快
RDB 缺点
- 如果备份时间间隔过长, RDB 会丢失较多的数据, 无法处理实时备份
- RDB 需要经常 fork() 以便使用子进程在磁盘上持久化, 增加 CPU 的负担
AOF
===如果 appendonly.aof 文件有错误, Redis 服务将会启动失败===
- redis-check-aof 检查 AOF 文件, --fix 参数修复文件的错误, 通常会丢弃文件中无法识别的命令
AOF(Append Only File), 将执行过的写命令全部记录下来, 在数据恢复时按照从前往后的顺序再将指令都执行一遍
appendonly yes启动 AOF 模式, 默认为 noappendfilename appendonly.aof默认文件名appenddirname appendonlydir默认存储目录appendfsync everysec持久化策略, 每秒钟执行一次, 可以修改为always和noalways每次将新命令附加到 AOF 时, 速度慢, 但是最安全no将写入策略权交给操作系统, 速度快, 但是不安全
no-appendfsync-on-rewrite noAOF 重写期间是否同步, 默认 no
Redis 7.0 支持使用新的 AOF 持久化方式, 包含三个文件, 当触发重写机制时, 自动创建新的基础文件和增量文件
- 以 appendfilename 为前缀命名的基础文件
appendfilename.*.base.rdb, 基础文件可以是 RDB 或 AOF - 以 appendfilename 为前缀命名的增量文件
appendfilename.*.incr.aof, 包含在上一个文件之后应用于数据集的其他命令 - 以 appendfilename 为前缀命名的清单文件
appendfilename.aof.manifest, 用于追踪文件及其创建和应用的顺序
如果同时开始 RDB 和 AOF 持久化时, Redis 重启时只会加载 AOF 文件, 不会加载 RDB 文件
AOF 优点
- AOF 更耐用, 可以在几秒钟内完成备份
- 当数据过大时, Redis 可以在后台自动重写 AOF, 节省空间
- AOF 实时性更好, 丢失数据更少, 并且支持配置写入策略
AOF 缺点
- 对于相同的数据集合, AOF 文件通常会比 RDB 文件大
- 在特定的 fsync 策略下, AOF 会比 RDB 略慢
- AOF 恢复速度比 RDB 慢
重写机制
auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100AOF 重写的基准值, 当达到 100% 时重写auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb当文件大小达到 64mb 的 100% 时重写BGREWRITEAOF 命令将会在后台开启 AOF 文件重写进程, 创建一个当前 AOF 文件的更小的优化版本, 如果重写失败不会丢失任何数据, 旧的 AOF 文件也不会受到影响
RDB 和 AOF 组合
fork 出的子进程先将共享的内存副本全量的以 RDB 格式写入 AOF 文件, 然后将 aof_rewrite_buf 重写缓冲区的增量命令以 AOF 格式写入到文件(在 RDB 格式数据的后面追加),
写入完成后通知主进程更新统计信息, 并将新的含有 RDB 格式和 AOF 格式的 AOF 文件替换旧的 AOF 文件. 新的 AOF 文件前半段是 RDB 格式的全量数据后半段是 AOF 格式的增量数据.
aof-use-rdb-preamble yes是否开始混合模式, 默认 yesRDB 做全量持久化
AOF 做增量持久化
主从复制
将一台 Redis 服务器的数据,复制到其他的 Redis 服务器. 前者称为主节点(Master/Leader),后者称为从节点(Slave/Follower), 数据的复制是单向的!只能由主节点复制到从节点(主节点以写为主、从节点以读为主)—— 读写分离.
===每台 Redis 服务器都是主节点===
一个主节点可以有 0 个或者多个从节点, 但每个从节点只能有一个主节点
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> INFO replication # 当前副本的信息 |
作用
- 数据冗余: 主从复制实现了数据的热备份, 是持久化之外的一种数据冗余的方式
- 故障恢复: 当主节点故障时, 从节点可以暂时替代主节点提供服务, 是一种服务冗余的方式
- 负载均衡: 在主从复制的基础上, 配合读写分离, 由主节点进行写操作, 从节点进行读操作, 分担节点的负载; 尤其是在多读少写的场景下, 通过多个从节点分担负载, 提高并发量
- 高可用(集群)基石: 主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础
复制原理
Redis 2.8 以上使用 PSYNC 命令完成同步
- 从节点向主节点发送
PSYNC命令, 如果从节点是首次连接主节点时会触发一次全量复制 - 接到
PSYNC命令的主节点会调用BGSAVE命令启动一个新线程创建 RDB 文件, 并使用缓冲区记录接下来执行的所有写命令 - 当 RDB 文件生成完毕后, 主节点向所有从节点发送 RDB 文件, 并在发送期间继续记录被执行的写命令
- 从节点接收到 RDB 文件后丢弃所有旧数据并载入这个文件
- 主节点将缓冲区记录的所有写命令发送给从节点执行
- 如果从节点断开连接后重连, 主节点仅将部分缺失的数据同步给从节点
- 全量复制: 从节点接收到数据库文件后, 将其全部加载到内存中
- 增量复制: 主节点将新的所有收集到的修改命令依次传给从节点, 完成同步
命令模式
===每台 Redis 服务器都是主节点===, 只用配置从服务器即可
运行时有效, 只在本次服务器运行时有效, 重启服务器后将会丢失配置信息
- 方式一: 启动 Redis 服务器时使用指定参数
redis-server --port 6380 --replicaof 127.0.0.1 6379 - 方式二: 连接 Redis 服务器使用内置命令
REPLICAOF host port
1 | # 设置关联主服务器 |
1 | # 主节点写入数据 |
提升从服务器角色
REPLICAOF NO ONE将从服务器更改为主服务器
配置文件模式
永久有效, 但是缺少可扩展性, 每次修改主从节点配置都需要重启 Redis 服务
redis.conf 基础配置,集群配置
1 | # 引入 redis 默认配置文件 |
- requirepass 认证
1 | # 第一种方式: 连接 redis 后使用内置命令 AUTH 命令认证 |
哨兵模式
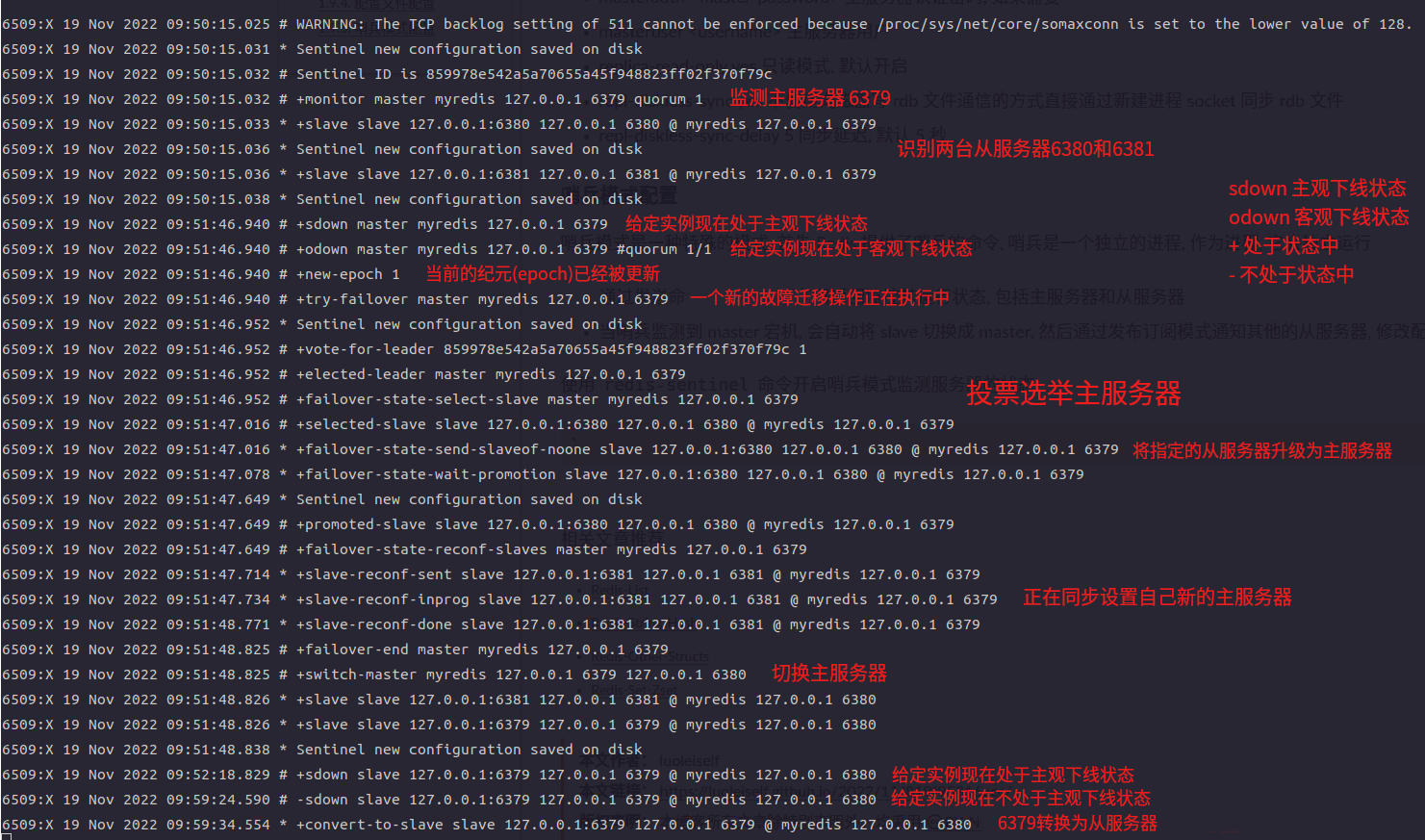
哨兵模式是一种特殊的模式, Redis 提供了启动哨兵的工具命令, 哨兵是一个独立的进程运行
哨兵节点通过发送
PING命令, 监控所有的主(从)节点的反馈运行状态当哨兵节点监控到 master 掉线并且其它多个哨兵节点确认 master 掉线后, 开始选取 leader 启动故障转移操作执行切换 master, 然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从节点, 修改配置文件并关联新的主节点
当 master 重连之后, 哨兵节点自动将 master 节点修改为 slave 模式
不能水平扩容, 不能动态的增、删节点
高可用特性会受到主节点的内存的限制
执行任务
- 监控: 定期检查主节点和从节点的健康状态, 包括发送
PING命令、检查返回结果和检测通信故障 - 自动故障转移: 当一个主节点不能正常工作时, Sentinel 会开始一次自动故障迁移操作, 它会将失效主节点的其中一个从节点升级为新的主节点, 并让失败的主节点的其他从节点改为复制新的主节点. 当客户端试图连接失效的主节点时, 集群也会向客户端返回新的主节点的地址, 使得集群可以使用新主节点代替失效节点
- 高可用性切换: 选举新的主节点后, 哨兵节点会自动将从节点切换为新的主节点, 并通知其它从节点更新复制目标
- 配置提供者: 当客户端连接到哨兵节点时, 哨兵节点可以根据 Redis 集群的配置信息, 将其重定向到正确的主节点
选举算法
首先, 领头 sentinel 根据从节点的信号反馈将从节点列表中失联的节点剔除, 按照从节点的优先级(replica-priority)进行排序并选择优先级最高的从节点, 如果有多个具有相同最高优先级的从节点, 那么, 领头 sentinel 将多个具有相同最高优先级的从节点按照复制偏移量(复制积压缓冲区中存储的写操作的字节占用累加, 主从节点进行 PSYNC 使用)进行排序并选择其中偏移量最大(偏移量最大保存的数据最新)的从节点, 如果有多个优先级最高, 复制偏移量最大的从节点, 那么 领头 sentinel 将按照从节点的运行 ID 进行排序并选择其中 ID 最小的从节点
replica-priority > replica-offset > run-ID
配置方式
- 方式一: 使用命令指定参数
redis-server /path/to/sentinel.conf --sentinel开启哨兵模式 - 方式二: 使用命令
redis-sentinel /path/to/sentinel.conf开启哨兵模式
sentinel.conf 配置文件
1 | protected-mode no # 保护模式, 默认 yes, 只能允许本机连接 |
一主三从哨兵配置
- 3 个哨兵配置
1 | # sentinel26379.conf |
- 3 台 redis 服务器配置
1 | # redis6379.conf |
- 根据配置文件启动所有服务
1 | [root@centos7 ~]# redis-server .config/redis6379.conf # 启动 redis 服务器 |
集群模式
Redis 3.0 支持
Redis Cluster 是一种服务器 Sharding(分片) 技术, Sharding 采用 slot 的概念, 一共分成 16384 个 slot, 对于每个进入 Redis 的键值对, 对 key 执行 CRC16(key) mod 16384 操作, 得到的结果就是对应的 slot.
Redis 集群中的每个 node 负责分摊这 16384 个 slot 中的一部分, 当动态增减 node 时, 需要将 16384 个 slot 再分配, slot 中的键值对也要迁移, 这一过程目前还处于半自动状态仍需要人工介入, 如果某个 node 发生故障, 则此 node 负责的 slot 也就失效, 整个集群将不能工作
官方推荐的方案是将 node 配置成主从结构, 即 1:n, 如果主节点失效, Redis Cluster 根据选举算法从 slave 节点中选择一个升级为主节点继续提供服务, 如果失效的主节点恢复正常后则作为新的主节点的从节点
Cluster Slot
从心跳包的大小、网络带宽、心跳并发、压缩率鞥维度考虑, 16384 个插槽更具有优势且能满足业务需求
- 正常的心跳数据包携带节点的完整配置, 它能以幂等方式来更新配置. 如果采用 16384 个插槽, 占空间 2KB(16384/8); 如果采用 65536 个插槽,占空间 8KB(65536/8). 8KB 的心跳包看似不大, 比起 16384 个插槽, 头大小增加了 4 倍,ping 消息的消息头太大, 浪费带宽
- Redis Cluster 不太可能扩展到超过 1000 个主节点, 太多可能导致网络拥堵
- 16384 个插槽比较合适, 当集群扩展到 1000 个节点时, 也能确保每个主节点有足够的插槽
集群特点
- 数据自动分片: 集群自动将数据分布到不同的节点上, 实现数据的均衡存储和负载均衡
- 自动故障转移: 当主节点发生故障时, 集群会自动进行故障检测, 并将从节点升级为新的主节点, 以保证系统的可用性
- 内部通信协议: 集集群使用 Gossip 协议进行节点之间的通信和状态更新, 确保集群的一致性和高效性
- 客户端路由: 客户端可以通过集群提供的路由机制, 自动将请求发送到正确的节点上, 实现透明访问
- 负载均衡: 在 Redis 集群中, 数据和请求会自动分布到不同的节点上, 实现负载均衡, 这样可以避免单个节点过载, 提高系统的稳定性和性能
- 扩展性好: 通过使用 Redis 集群, 可以便利地扩展系统的容量和性能, 将数据和请求分布到多个节点上, 提高整体系统的吞吐量和承载能力
- 高可用性: 通过 Redis 集群, 可以将数据分布到多个节点上, 实现数据的冗余备份和容错能力, 当部分节点不可用时, 集群仍然可以继续提供服务, 保证系统的可用性
命令
redis-cli --cluster help # 查看集群命令帮助信息
redis-cli --cluster create host1:port1 … hostN:portN # 创建指定 IP 和 Port 的服务器作为集群
- --cluster-replicas <arg> # 指定集群中主节点和从节点数量的比例, 1 表示 1:1
redis-cli --cluster add-node new_host:new_port existing_host:existing_port # 添加集群节点
- --cluster-slave # 添加集群节点从服务器
- --cluster-master-id <arg> # 添加到指定主服务器下
redis-cli --cluster reshard <host:port> # 重新分配节点的 hash 插槽
- --cluster-from <arg> # 已有节点 id, 多个 id 之间使用半角逗号分隔
- --cluster-to <arg> # 新节点 id
- --cluster-slots <arg> # 新节点的 hash 槽数量
redis-cli --cluster rebalance <host:port> # 重新分配节点
- --cluster-weight <node1=w1…nodeN=wN> # 分配节点权重
- --cluster-timeout <arg> # 节点超时时间
- --cluster-threshold <arg> # 节点阈值
redis-cli --cluster import host:port # 导入指定节点
- --cluster-from <arg> # 从指定 id
- --cluster-from-user <arg> # 指定用户名
- --cluster-from-pass <arg> # 指定密码
redis-cli --cluster info <host:port> # 查看指定节点信息
redis-cli --cluster check <host:port> # 检查指定节点
redis-cli --cluster del-node host:port node_id # 删除集群节点
redis-cli --cluster call host:port command arg arg … arg # 集群节点执行指定命令
- --cluster-only-masters 所有主节点
- --cluster-only-replicas 所有副本节点
1
2# 在所有主节点上执行加载的命令
[root@centos7 workspace]# redis-cli --cluster --cluster-only-masters call host:port FUNCTION LOAD ...redis-cli --cluster set-timeout host:port milliseconds # 设置节点的超时时间
redis-cli --cluster backup host:port backup_directory # 备份节点数据到指定目录
使用 redis-cli -c -p port 命令接入集群节点
集群部署
编辑配置文件
创建 Redis 服务器配置文件, 引入默认配置文件并覆盖配置项, 开启集群模式
创建 cluster6379.conf, cluster6380.conf, cluster6381.conf, cluster6382.conf, cluster6383.conf, cluster6384.conf 6 个文件
修改其中的 bind, port, pidfile, cluster-enabled, cluster-config-file
集群配置, 基础配置
1 | # # 引入 redis 默认配置文件 |
启动 Redis 服务器
启动所有的 redis 服务器, 使用 ps -ef | grep redis 命令查看 redis 服务器进程
redis 进程后中括号中的 cluster 表示 redis 工作在集群模式下, 需要进一步配置 redis 的集群关系
1 | [root@centos7 redis-cluster]# redis-server cluster6379.conf |
创建集群节点
使用 redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas arg hostN:portN 命令创建集群节点, arg 参数表示集群主从节点的数量比例, 1 表示 1:1
创建过程中提示输入 yes 表示接受当前配置信息并写入指定文件中, 最后输出 [OK] All 16384 slots covered. 表示集群创建完成
1 | [root@centos7 redis-cluster]# redis-cli --cluster create --cluster-replicas 1 \ |
连接 Redis 服务器
使用 redis-cli -c -p port 命令接入集群节点
- -c 以集群模式接入
1 | [root@centos7 redis-cluster]# redis-cli -c -p 6379 |
集群命令
- CLUSTER HELP 在 Redis 命令行中查看所有集群操作命令
1 | 127.0.0.1:6380> CLUSTER HELP |
- CLUSTER INFO
- CLUSTER SLOTS 返回集群中 hash 槽的详细信息, redis 7.0 开始使用 CLUSTER SHARDS 命令代替
- CLUSTER REPLICAS <node-id> 列出指定节点的所有副本节点的信息, 功能和 CLUSTER NODES 类似
- CLUSTER NODES
- CLUSTER REPLICATE <node-id> 配置当前节点为指定主节点的从节点
- CLUSTER KEYSLOT <somekey> 计算指定 key 所在的 hash 槽
- CLUSTER COUNTKEYSINSLOT <slot> 统计集群中 hash 槽中存储的 key 的数量
- CLUSTER FAILOVER 手动启动集群故障转移操作, 此命令只能发送给集群从节点
- CLUSTER FLUSHSLOTS 清空当前节点的所有插槽
查看节点信息
- 方式一: 命令行中使用
redis-cli --cluster info host:port命令查看指定节点的信息
1 | [root@centos7 redis-cluster]# redis-cli --cluster info 127.0.0.1:6380 |
- 方式二: 在 Redis 命令行中使用
CLUSTER INFO|SLOTS|NODES查看节点信息
1 | # 查看当前节点信息 |
数据操作
设置键时, 根据键散列后的值所在的插槽位置自动切换到插槽所在的节点上
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> KEYS * |
测试节点
使用 kill 命令停止端口号为 6381 的 redis 进程时, 集群切换 6381 的状态为失联, 同时将从节点 6384 升级为主节点, 等到 6381 恢复后变为 6384 的从节点
1 | 127.0.0.1:6379> CLUSTER NODES |
查看节点配置文件
1 | [root@centos7 redis-cluster]# cat nodes-6381.conf |
添加新节点
按照 编辑配置文件 创建并修改 cluster6385.conf 文件
启动服务器 redis-server cluster6385.conf, 同时查看服务器是否正常启动
- 使用命令
redis-cli --cluster add-node --cluster-slave 127.0.0.1:6385 127.0.0.1:6379将 6385 添加为 6379 的从节点
1 | # 向 6379 节点添加新的从节点 |
- 查看节点 6379 的信息, 显示 2 个从节点
1 | # 查看节点信息 |
集群优点
- 实现扩容
- 分担压力
- 无中心配置相对简单
集群缺点
- 多建操作不支持, 例如
MSET命令设置多个键不支持, 需要使用分组方式MSET name{user} zhangsan age{user} 20 addr{user} beijing - 多键的 Redis 事务不支持
- Lua 脚本不支持
- 迁移方案需要整体迁移而不是逐步过渡, 复杂度较大